Monoclonal antibody pairs against SARS-CoV-2 for rapid antigen test development
- PMID: 35358198
- PMCID: PMC9004783
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010311
Monoclonal antibody pairs against SARS-CoV-2 for rapid antigen test development
Abstract
Background: The focus on laboratory-based diagnosis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) warrants alternative public health tools such as rapid antigen tests. While there are a number of commercially available antigen tests to detect severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), all cross-react with the genetically similar SARS-CoV-1 or require an instrument for results interpretation.
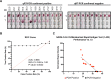
Methodology/principal findings: We developed and validated rapid antigen tests that use pairs of murine-derived monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), along with gold nanoparticles, to detect SARS-CoV-2 with or without cross-reaction to SARS-CoV-1 and other coronaviruses. In this development, we demonstrate a robust antibody screening methodology for the selection of mAb pairs that can recognize SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) and nucleocapsid (N) proteins. Linear epitope mapping of the mAbs helped elucidate SARS-CoV-2 S and N interactions in lateral flow chromatography. A candidate rapid antigen test for SARS-CoV-2 N was validated using nasal swab specimens that were confirmed positive or negative by quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Test results were image-captured using a mobile phone and normalized signal pixel intensities were calculated; signal intensities were inversely correlated to RT-PCR cycle threshold (Ct) value.
Conclusion/significance: Overall, our results suggest that the rapid antigen test is optimized to detect SARS-CoV-2 N during the acute phase of COVID-19. The rapid antigen tests developed in this study are alternative tools for wide scale public health surveillance of COVID-19.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests:NS, AR, ARG, IB and BBH are employed by or affiliated with E25Bio, Inc., a company that develops rapid diagnostic tests for fever causing infectious agents.
Figures




References
-
- Medicine JHU. Coronavirus Resource Center. Available from: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html.
-
- Ivorra B, Ferrandez MR, Vela-Perez M, Ramos AM. Mathematical modeling of the spread of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) taking into account the undetected infections. The case of China. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul. 2020;88:105303. Epub 2020/05/02. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2020.105303 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC7190554. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

