Management of cardiac diseases in liver transplant recipients: Comprehensive review and multidisciplinary practice-based recommendations
- PMID: 35359027
- PMCID: PMC9522925
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.17049
Management of cardiac diseases in liver transplant recipients: Comprehensive review and multidisciplinary practice-based recommendations
Abstract
Cardiac diseases are one of the most common causes of morbidity and mortality following liver transplantation (LT). Prior studies have shown that cardiac diseases affect close to one-third of liver transplant recipients (LTRs) long term and that their incidence has been on the rise. This rise is expected to continue as more patients with advanced age and/or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis undergo LT. In view of the increasing disease burden, a multidisciplinary initiative was developed to critically review the existing literature (between January 1, 1990 and March 17, 2021) surrounding epidemiology, risk assessment, and risk mitigation of coronary heart disease, arrhythmia, heart failure, and valvular heart disease and formulate practice-based recommendations accordingly. In this review, the expert panel emphasizes the importance of optimizing management of metabolic syndrome and its components in LTRs and highlights the cardioprotective potential for the newer diabetes medications (e.g., sodium glucose transporter-2 inhibitors) in this high-risk population. Tailoring the multidisciplinary management of cardiac diseases in LTRs to the cardiometabolic risk profile of the individual patient is critical. The review also outlines numerous knowledge gaps to pave the road for future research in this sphere with the ultimate goal of improving clinical outcomes.
Keywords: cardiac outcomes; cirrhotic cardiomyopathy; coronary artery disease; liver transplant.
Darshana M. Dadhania and Lisa B. VanWagner contributed equally.© 2022 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
B.E.F. is a consultant for W.L. Gore & Associates and Cook Medical.
L.B.V. receives investigator-initiated grant support from W.L. Gore & Associates, grant support from Intercept Pharmaceuticals, and grant support from AMRA Medical outside the scope of this work. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

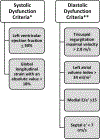

References
-
- Watt KD, Coss E, Pedersen RA, Dierkhising R, Heimbach JK, Charlton MR. Pretransplant serum troponin levels are highly predictive of patient and graft survival following liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 2010;16(8):990–998. - PubMed
-
- D’Avola D, Cuervas-Mons V, Marti J, et al. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality after liver transplantation: The protective role of mycophenolate mofetil. Liver Transpl 2017;23(4):498–509. - PubMed
-
- Fussner LA, Heimbach JK, Fan C, et al. Cardiovascular disease after liver transplantation: When, What, and Who Is at Risk. Liver Transpl 2015;21(7):889–896. - PubMed
-
- Durand F How to improve long-term outcome after liver transplantation? Liver Int 2018;38 Suppl 1:134–138. - PubMed

