Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Large Granular Lymphocytic Leukemia
- PMID: 35359386
- PMCID: PMC8960188
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.849917
Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Large Granular Lymphocytic Leukemia
Abstract
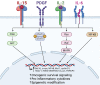
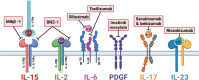
Large granular lymphocytic leukemia (LGLL) is a lymphoproliferative disorder of older adults characterized by the clonal expansion of cytotoxic T/natural killer cells due to constitutive pro-survival signaling. In recent years, it has become clear that cytokines and their receptors are aberrantly expressed in LGLL cells. The exact initiation process of LGLL is unknown, although several cytokine-driven mechanisms have emerged. Elevated levels of several cytokines, including interleukin-15 (IL-15) and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), have been described in LGLL patients. Evidence from humans and animal models has shown that cytokines may also contribute to the co-occurrence of a wide range of autoimmune diseases seen in patients with LGLL. The goal of this review is to provide a comprehensive analysis of the link between cytokines and pro-survival signaling in LGLL and to discuss the various strategies and research approaches that are being utilized to study this link. This review will also highlight the importance of cytokine-targeted therapeutics in the treatment of LGLL.
Keywords: LGLL; cytokines; growth factors; interleukins; therapy.
Copyright © 2022 Isabelle, Boles, Chakravarti, Porcu, Brammer and Mishra.
Conflict of interest statement
JB, AM, and PP have received funding from pharmaceutical companies for research and clinical trials. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

