Degenerative Nucleus Pulposus Cells Derived Exosomes Promoted Cartilage Endplate Cells Apoptosis and Aggravated Intervertebral Disc Degeneration
- PMID: 35359595
- PMCID: PMC8963919
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.835976
Degenerative Nucleus Pulposus Cells Derived Exosomes Promoted Cartilage Endplate Cells Apoptosis and Aggravated Intervertebral Disc Degeneration
Abstract
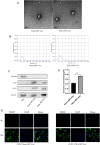
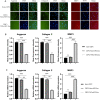
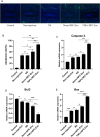
Intervertebral disc (IVD) degeneration is a complex multifactorial disease model, which pathogenesis has not been fully defined. There are few studies on the information interaction between nucleus pulposus (NP) cells and cartilage endplate (CEP) cells. Exosomes, as a carrier of information communication between cells, have become a research hotspot recently. The purpose of this study was to explore whether degenerative NP cells-derived exosomes promoted CEP cells apoptosis and aggravated IVD degeneration. The degenerative NP cells model was induced by TNFα. NPC exosomes were isolated from the supernatant of the NP cell culture medium. The viability of NP cells and CEP cells was examined by CCK-8 assays. The exosomes were identified by TEM, NTA, and western blot. Extracellular matrix (ECM) metabolism was measured by cellular immunofluorescence and qRT-PCR. Apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry and TUNEL. X-ray and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), as well as hematoxylin-eosin (H&E), Safranine O-Green staining was adopted to evaluate IVD degeneration grades. TNFα had a minor impact on NPC viability but inhibited ECM synthesis and promoted ECM degradation. TNFα-NPC-Exo had less effect on CEPC proliferation but promoted CEPC apoptosis and affect ECM metabolism, inhibiting aggrecan and collagen II expression and enhancing MMP-3 expression. TNFα-NPC-Exo aggravates IVD degeneration in a rat model and promoted CEPC apoptosis. In conclusion, this study demonstrated that degenerated NPC-exosome could induce apoptosis of CEPCs, inhibit ECM synthesis, and promote ECM degradation. In addition, it was proved that degenerated NPC-exosome aggravates IVD degeneration.
Keywords: apoptosis; cartilage endplate; exosome; intervertebral disc degeneration; nucleus pulposus.
Copyright © 2022 Feng, Li, Su and Tan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

