High Serum Levels of Otolin-1 in Patients With Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Predict Recurrence
- PMID: 35359660
- PMCID: PMC8963966
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.841677
High Serum Levels of Otolin-1 in Patients With Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Predict Recurrence
Abstract
Background: Otolin-1 is an inner ear-specific protein that is exclusively expressed in otoconia and vestibule and cochlea cells. Recent investigations reported that otolin-1 can cross the blood-labyrinthine barrier and that the levels in serum well-reflected otolith status. Serum otolin-1 levels in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) are significantly elevated compared with healthy controls. We aimed to explore whether otolin-1 can also serve as a biomarker for predicting BPPV recurrence.
Method: Patients at our institution with new-onset of idiopathic BPPV between May, 2017 and May, 2018 were recruited and followed up for 2 years. All demographic data of the patients were collected, and serum levels of otolin-1 and other laboratory indicators were measured and compared according to the recurrence status.
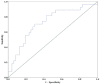
Results: A total of 74 patients, who met the inclusion criteria were enrolled in this study, of which 27 (36.5%) patients had suffered one or more episodes of recurrence after undergoing canal repositioning treatments during the study. The serum levels of otolin-1 in patients with recurrent BPPV were significantly higher than those in patients without recurrent BPPV (363.9 vs. 309.8 pg/ml, p = 0.001). In multivariate analysis comparing the second to fourth quartiles (Q2-Q4) against the first quartile (Q1) of otolin-1, the level of otolin-1 in Q4 could significantly predict BPPV recurrence, and the odds ratio (OR) was elevated by approximately 812% (OR = 9.12; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.44-57.9; p = 0.019).
Conclusion: High serum levels of otolin-1 were associated with an increased risk of BPPV recurrence, and further investigation is required to confirm this association and clarify the exact mechanism.
Keywords: benign paroxysmal positional vertigo; biomarker; canalith repositioning procedure; otolin-1; recurrence.
Copyright © 2022 Fan, Hu, Han, Lu, Liu, Zhou, Yan and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum Otoconin-90 and Otolin-1 Concentrations in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo.Biomolecules. 2024 Oct 10;14(10):1279. doi: 10.3390/biom14101279. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39456211 Free PMC article.
-
Association between otolin-1 and benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2022 Dec 15;13:950023. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.950023. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36601298 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Otolin-1 in Serum as a Potential Biomarker for Idiopathic Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Episodes.Front Neurol. 2020 May 13;11:367. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00367. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32477244 Free PMC article.
-
An evaluation of serum Otolin-1 & Vitamin-D in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo.J Vestib Res. 2021;31(6):433-440. doi: 10.3233/VES-201601. J Vestib Res. 2021. PMID: 33720865
-
Association of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo with vitamin D deficiency: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018 Nov;275(11):2705-2711. doi: 10.1007/s00405-018-5146-6. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018. PMID: 30302575
Cited by
-
Advances in otolith-related protein research.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jul 26;16:956200. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.956200. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35958995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum Otoconin-90 and Otolin-1 Concentrations in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo.Biomolecules. 2024 Oct 10;14(10):1279. doi: 10.3390/biom14101279. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39456211 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of brandt-daroff exercises in the treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024 Jul;281(7):3371-3384. doi: 10.1007/s00405-024-08502-6. Epub 2024 Feb 11. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 38341824
-
Association between otolin-1 and benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2022 Dec 15;13:950023. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.950023. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36601298 Free PMC article.
-
Residual dizziness after BPPV management: exploring pathophysiology and treatment beyond canalith repositioning maneuvers.Front Neurol. 2024 May 24;15:1382196. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1382196. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38854956 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lindell E, Kollén L, Johansson M, Karlsson T, Rydén L, Falk Erhag H, et al. . Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, dizziness, and health-related quality of life among older adults in a population-based setting. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. (2021) 278:1637–44. 10.1007/s00405-020-06357-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous