The Association Between the China's Economic Development and the Passing Rate of National Physical Fitness Standards for Elderly People Aged 60-69 From 2000 to 2020
- PMID: 35359759
- PMCID: PMC8961805
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.857691
The Association Between the China's Economic Development and the Passing Rate of National Physical Fitness Standards for Elderly People Aged 60-69 From 2000 to 2020
Abstract
Objective: According to the seventh demographic census, China's elderly population reached 260 million, accounting for 18.7% of the total population, indicating that China is on the verge of transitioning from a relatively mild aging to a moderately aging society, and an aging society inevitably brings concerns about the elderly people's health. The purpose of this study was to better understand the effect of economic development on the physical fitness of the elderly people aged 60-69 in China during the first two decades of the twenty-first century, as well as to establish a correlation between China's gross domestic product (GDP) and changes in the elderly people's passing rate of national physical fitness standards.
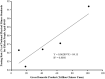
Methods: A linear regression analysis was performed on the data of GDP and the passing rate of national physical fitness standards of Chinese elderly people aged 60-69 in 2000, 2005, 2010, 2014, and 2020.
Results: The passing rate of national physical fitness standards for elderly people aged 60-69 increased linearly (R2 = 80.56%, p < 0.05), indicating that the physical fitness of the elderly tends to increase steadily with GDP expansion.
Conclusions: Between 2000 and 2020, the annual improvement in the physical fitness of the elderly people in China is inextricably linked to rapid economic development. Increased financial investments in public sports services and a corresponding national fitness plan all contribute to an overall improvement in the physical fitness of the elderly people. This outcome is the effect of fiscal and policy coordination, which may represent a distinctive Chinese model and contribution to the global effort to manage and improve population physical fitness.
Keywords: GDP; policy coordination; population aging; public financing; public health; spillovers; sports industry.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Agudamu, Bu, Akpinar and Jabucanin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- García-Hermoso A, Ezzatvar Y, López-Gil JF, Ramírez-Vélez R, Olloquequi J, Izquierdo M. Is adherence to the Mediterranean diet associated with healthy habits and physical fitness? A systematic review and meta-analysis including 565 421 youths. Br J Nutr. 2020:1–12. 10.1017/S0007114520004894 - DOI - PubMed