Hypericum lanceolatum Lam. Medicinal Plant: Potential Toxicity and Therapeutic Effects Based on a Zebrafish Model
- PMID: 35359845
- PMCID: PMC8963451
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.832928
Hypericum lanceolatum Lam. Medicinal Plant: Potential Toxicity and Therapeutic Effects Based on a Zebrafish Model
Abstract
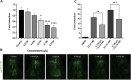
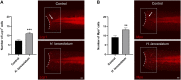
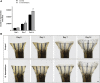
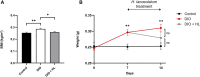
Hypericum lanceolatum Lam. (H. lanceolatum) is a traditional medicinal plant from Reunion Island used for its pleiotropic effects mainly related to its antioxidant activity. The present work aimed to 1) determine the potential toxicity of the plant aqueous extract in vivo and 2) investigate its putative biological properties using several zebrafish models of oxidative stress, regeneration, estrogenicity, neurogenesis and metabolic disorders. First, we characterized the polyphenolic composition by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and identified chlorogenic acid isomers, quercetin and kaempferol derivatives as the major compounds. We then evaluated for the first time the toxicity of an aqueous extract of H. lanceolatum and determined a maximum non-toxic concentration (MNTC) in zebrafish eleutheroembryos from 0 to 96 hpf following OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development) guidelines. This MNTC test was also determined on hatched eleutheroembryos after 2 days of treatment (from 3 to 5 dpf). In our study, the anti-estrogenic effects of H. lanceolatum are supported by the data from the EASZY assay. In a tail amputation model, we showed that H. lanceolatum at its MNTC displays antioxidant properties, favors immune cell recruitment and tissue regeneration. Our results also highlighted its beneficial effects in metabolic disorders. Indeed, H. lanceolatum efficiently reduces lipid accumulation and body mass index in overfed larva- and adult-models, respectively. In addition, we show that H. lanceolatum did not improve fasting blood glucose levels in a hyperglycemic zebrafish model but surprisingly inhibited neurogenesis impairment observed in diabetic conditions. In conclusion, our study highlights the antioxidant, pro-regenerative, anti-lipid accumulation and pro-neurogenic effects of H. lanceolatum in vivo and supports the use of this traditional medicinal plant as a potential alternative in the prevention and/or treatment of metabolic disorders.
Keywords: LC MS/MS; Toxicity; Zebrafish; diabetes; neurogenesis; obesity; regeneration.
Copyright © 2022 Gence, Fernezelian, Bringart, Veeren, Christophe, Brion, Meilhac, Bascands and Diotel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



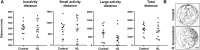




References
-
- Agence Nationale De Sécurité Du Médicament Et Des Produits De Santé (2021). La Pharmacopée Française. [Online]. Available at: https://ansm.sante.fr/documents/reference/pharmacopee/la-pharmacopee-fra... . (Accessed, 2021).
-
- Aplamedom Reunion (2021). Les plantes médicinales de La Réunion. [Online]. Available at: https://aplamedom.org/les-plantes-medicinales-de-la-reunion/ . (Accessed, 2021).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

