Perspectives on the Efficacy of Benralizumab for Treatment of Eosinophilic Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis
- PMID: 35359852
- PMCID: PMC8960447
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.865318
Perspectives on the Efficacy of Benralizumab for Treatment of Eosinophilic Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis
Abstract
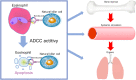
Two types of interleukin (IL)-5 antibody biologics, anti-IL-5 antibodies (mepolizumab) and anti-IL-5α receptor antibodies (benralizumab), are indicated for severe asthma. While high-dose mepolizumab is also indicated for EGPA, benralizumab is indicated only for severe asthma. Benralizumab is characterized by antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity activity, giving them specific and rapid anti-IL-5α receptor binding abilities and the ability to target a high number of eosinophils in tissues as well as peripheral blood. Recently, reports on the efficacy of benralizumab as a treatment for EGPA have been published, along with reports on some cases that are difficult to treat with existing oral corticosteroids and mepolizumab. Therefore, we focus on the perspective of the efficacy and safety of benralizumab as a treatment for EGPA patients with steroid dependence in this review. A total of 41 patients with EGPA were treated with benralizumab. After the introduction of benralizumab, oral corticosteroids could be reduced to 10 mg/day or less in all cases and to less than 5 mg/day in 80% or more of the cases. Discontinuation of oral corticosteroids was achieved in more than 40% of patients with EGPA. Benralizumab was effective in patients with mepolizumab-refractory EGPA and intractable cardiac and neuropathy complications. Efficient elimination of eosinophils is expected to improve the remission rate of EGPA with benralizumab treatment. Although the total number of patients was small, benralizumab was safe and tolerable in a wide range of age groups, suggesting efficacy in severe cases with EGPA.
Keywords: asthma; benralizumab; cardiomyopathy; eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis; mepolizumab; mononeuritis multiplex; neuropathy.
Copyright © 2022 Koga, Aoki-Saito, Kamide, Sato, Tsurumaki, Yatomi, Ishizuka and Hisada.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

