Safety monitoring of COVID-19 vaccines in Japan
- PMID: 35359913
- PMCID: PMC8960038
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2022.100442
Safety monitoring of COVID-19 vaccines in Japan
Abstract
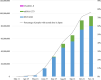
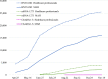
The assessment of the efficacy and safety of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines in actual practice is extremely important, and monitoring efforts are being implemented worldwide. In Japan, a joint council in the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare is held every two to three weeks to summarise information on the adverse events following COVID-19 vaccination, with careful assessment of individual case safety reports and comparison with background incidence rates. In 2021, the joint council mainly reviewed anaphylaxis, death, myocarditis/pericarditis, and thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome. These activities resulted in several safety-related regulatory actions, including the revision of vaccine package inserts with warnings about myocarditis/pericarditis. International sharing of vaccine safety information, as well as details of the evaluation systems, is important for international discussion and decision-making on better safety monitoring of COVID-19 vaccines.
Keywords: COVID-19; Epidemiology; Health policy; Pharmacovigilance; Vaccines.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
AO receives grants from Eisai Co., Ltd, SHIONOGI & CO., LTD., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co, Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Pfizer Japan Inc. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- WHO Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) dashboard; 2020. https://covid19.who.int/. Accessed 10 January 2022.
-
- Ritchie H, Mathieu E, Rodés-Guirao L, et al. Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19); 2020. published online March 5. https://ourworldindata.org/covid-vaccinations?country=JPN. Accessed 10 January 2022.
-
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Revision of Precautions. Coronavirus modified uridine RNA vaccine (SARS-CoV-2) (Comirnaty intramuscular injection); 2021. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000243865.pdf. Accessed 10 January 2022.
-
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Revision of Precautions. Coronavirus modified uridine RNA vaccine (SARS-CoV-2) (COVID-19 Vaccine Moderna Intramuscular Injection); 2021. https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000243866.pdf. Accessed 10 January 2022.
-
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Health Sciences Council (the Immunization and Vaccination committee - the committee on Adverse Reactions) [in Japanese]. https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/shingi/shingi-kousei_284075.html. Accessed 4 March 2022.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

