TMT-Based Quantitative Proteomics Analysis of Synovial Fluid-Derived Exosomes in Inflammatory Arthritis
- PMID: 35359923
- PMCID: PMC8961740
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.800902
TMT-Based Quantitative Proteomics Analysis of Synovial Fluid-Derived Exosomes in Inflammatory Arthritis
Abstract
Objectives: To compare the proteomics of synovial fluid (SF)-derived exosomes in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA), gout, and osteoarthritis (OA) patients.
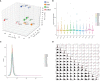
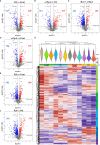
Methods: Exosomes were separated from SF by the Exoquick kit combined ultracentrifugation method. Tandem mass tags (TMT)-labeled liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) technology was used to analyze the proteomics of SF-derived exosomes. Volcano plot, hierarchical cluster, gene ontology (GO), and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis were conducted.
Results: A total of 1,678 credible proteins were detected. Sixty-nine differentially expressed proteins were found in gout, compared with OA, axSpA, and RA simultaneously. Twenty-five proteins were found highly expressed in gout uniquely, lysozyme C and protein S100-A9 included, whose bioinformatic analysis was significantly involved in "neutrophil degranulation" and "prion diseases". Eighty-four differentially expressed proteins were found in axSpA, compared with OA, gout, and RA simultaneously. Thirty-nine proteins were found highly expressed in axSpA uniquely, RNA-binding protein 8A and protein transport protein Sec24C included, whose bioinformatic analysis was significantly involved in "acute-phase response" and "citrate cycle". One hundred and eighty-four differentially expressed proteins were found in RA, compared with OA, gout, and axSpA simultaneously. Twenty-eight proteins were found highly expressed in RA uniquely, pregnancy zone protein (PZP) and stromelysin-1 included, whose bioinformatic analysis was significantly involved in "serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity" and "complement and coagulation cascades". Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) result showed that the exosome-derived PZP level of SF in RA was higher than that in OA (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Our study for the first time described the protein profiles of SF-derived exosomes in RA, axSpA, gout, and OA patients. Some potential biomarkers and hypothetical molecular mechanisms were proposed, which may provide helpful diagnostic and therapeutic insights for inflammatory arthritis (IA).
Keywords: biomarkers; exosomes; inflammatory arthritis; proteomics analysis; synovial fluid.
Copyright © 2022 Huang, Liu, Huang, Sun, Ji, Huang, Li, Huang, Deng and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Radner H, Ramiro S, Buchbinder R, Landewé RB, van der Heijde D, Aletaha D. Pain Management for Inflammatory Arthritis (Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis and Other Spondylarthritis) and Gastrointestinal or Liver Comorbidity. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (2012) 1:CD008951. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008951.pub2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Scher JU, Ubeda C, Artacho A, Attur M, Isaac S, Reddy SM, et al. . Decreased Bacterial Diversity Characterizes the Altered Gut Microbiota in Patients With Psoriatic Arthritis, Resembling Dysbiosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Arthritis Rheum (Hoboken NJ) (2015) 67(1):128–39. doi: 10.1002/art.38892 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

