Computational Mechanism of Methyl Levulinate Conversion to γ-Valerolactone on UiO-66 Metal Organic Frameworks
- PMID: 35360051
- PMCID: PMC8942187
- DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c08021
Computational Mechanism of Methyl Levulinate Conversion to γ-Valerolactone on UiO-66 Metal Organic Frameworks
Abstract
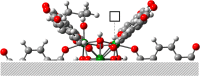
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are gaining importance in the field of biomass conversion and valorization due to their porosity, well-defined active sites, and broad tunability. But for a proper catalyst design, we first need detailed insight of the system at the atomic level. Herein, we present the reaction mechanism of methyl levulinate to γ-valerolactone on Zr-based UiO-66 by means of periodic density functional theory (DFT). We demonstrate the role of Zr-based nodes in the catalytic transfer hydrogenation (CTH) and cyclization steps. From there, we perform a computational screening to reveal key catalyst modifications to improve the process, such as node doping and linker exchange.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Combined DFT and Kinetic Monte Carlo Study of UiO-66 Catalysts for γ-Valerolactone Production.J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2024 Jan 12;128(3):1049-1057. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.3c06053. eCollection 2024 Jan 25. J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 38293690 Free PMC article.
-
Water-Tolerant DUT-Series Metal-Organic Frameworks: A Theoretical-Experimental Study for the Chemical Fixation of CO2 and Catalytic Transfer Hydrogenation of Ethyl Levulinate to γ-Valerolactone.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019 Nov 6;11(44):41458-41471. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b16834. Epub 2019 Oct 28. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019. PMID: 31613085
-
Enhancing the conversion of ethyl levulinate to γ-valerolactone over Ru/UiO-66 by introducing sulfonic groups into the framework.RSC Adv. 2018 May 4;8(30):16611-16618. doi: 10.1039/c8ra01314d. eCollection 2018 May 3. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35540507 Free PMC article.
-
Quantum Mechanical Calculations for Biomass Valorization over Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs).Chem Asian J. 2021 May 3;16(9):1049-1056. doi: 10.1002/asia.202001371. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Chem Asian J. 2021. PMID: 33651485 Review.
-
Effects of Solid Acid Supports on the Bifunctional Catalysis of Levulinic Acid to γ-Valerolactone: Catalytic Activity and Stability.Chem Asian J. 2020 Apr 17;15(8):1182-1201. doi: 10.1002/asia.202000006. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Chem Asian J. 2020. PMID: 32012471 Review.
Cited by
-
MOFganic Chemistry: Challenges and Opportunities for Metal-Organic Frameworks in Synthetic Organic Chemistry.Chem Mater. 2023 Jul 11;35(13):4883-4896. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.3c00741. Epub 2023 Jun 21. Chem Mater. 2023. PMID: 38222037 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling and Thermodynamic Studies of γ-Valerolactone Production from Bio-derived Methyl Levulinate.Glob Chall. 2023 Feb 22;7(4):2200208. doi: 10.1002/gch2.202200208. eCollection 2023 Apr. Glob Chall. 2023. PMID: 37020618 Free PMC article.
-
Combined DFT and Kinetic Monte Carlo Study of UiO-66 Catalysts for γ-Valerolactone Production.J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2024 Jan 12;128(3):1049-1057. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.3c06053. eCollection 2024 Jan 25. J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 38293690 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bozell J. J.; Petersen G. R. Technology Development for the Production of Biobased Products from Biorefinery Carbohydrates—The US Department of Energy’s “Top 10” Revisited. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 539–554. 10.1039/b922014c. - DOI
-
- Alonso D. M.; Wettstein S. G.; Dumesic J. A. Gamma-Valerolactone, a Sustainable Platform Molecule Derived from Lignocellulosic Biomass. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 584–595. 10.1039/c3gc37065h. - DOI
-
- Gilkey M. J.; Xu B. Heterogeneous Catalytic Transfer Hydrogenation as an Effective Pathway in Biomass Upgrading. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 1420–1436. 10.1021/acscatal.5b02171. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
