Hypoxia Induces Saturated Fatty Acids Accumulation and Reduces Unsaturated Fatty Acids Independently of Reverse Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle in L6 Myotubes
- PMID: 35360057
- PMCID: PMC8963465
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.663625
Hypoxia Induces Saturated Fatty Acids Accumulation and Reduces Unsaturated Fatty Acids Independently of Reverse Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle in L6 Myotubes
Abstract
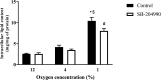
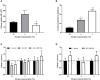
Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, characterized by repetitive episodes of tissue hypoxia, is associated with several metabolic impairments. Role of fatty acids and lipids attracts attention in its pathogenesis for their metabolic effects. Parallelly, hypoxia-induced activation of reverse tricarboxylic acid cycle (rTCA) with reductive glutamine metabolism provides precursor molecules for de novo lipogenesis. Gas-permeable cultureware was used to culture L6-myotubes in chronic hypoxia (12%, 4% and 1% O2) with 13C labelled glutamine and inhibitors of glutamine uptake or rTCA-mediated lipogenesis. We investigated changes in lipidomic profile, 13C appearance in rTCA-related metabolites, gene and protein expression of rTCA-related proteins and glutamine transporters, glucose uptake and lactate production. Lipid content increased by 308% at 1% O2, predominantly composed of saturated fatty acids, while triacylglyceroles containing unsaturated fatty acids and membrane lipids (phosphatidylcholines, phosphatidylethanolamines, phosphatidylinositol) decreased by 20-70%. rTCA labelling of malate, citrate and 2-hydroxyglutarate increased by 4.7-fold, 2.2-fold and 1.9-fold in 1% O2, respectively. ATP-dependent citrate lyase inhibition in 1% O2 decreased lipid amount by 23% and increased intensity of triacylglyceroles containing unsaturated fatty acids by 56-80%. Lactate production increased with hypoxia. Glucose uptake dropped by 75% with progression of hypoxia from 4% to 1% O2. Protein expression remained unchanged. Altogether, hypoxia modified cell metabolism leading to lipid composition alteration and rTCA activation.
Keywords: L6 myotubes; glutamin; hypoxia; lipids; obstructive sleep apnea; reverse TCA.
Copyright © 2022 Vacek, Dvorak, Bechynska, Kosek, Elkalaf, Trinh, Fiserova, Pospisilova, Slovakova, Vitek, Hajslova and Polak.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
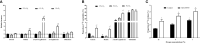
Similar articles
-
Contribution of glucose and glutamine to hypoxia-induced lipid synthesis decreases, while contribution of acetate increases, during 3T3-L1 differentiation.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 15;14(1):28193. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79458-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39548264 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Serum and Hypoxia on Incorporation of [(14)C]-D-Glucose or [(14)C]-L-Glutamine into Lipids and Lactate in Murine Glioblastoma Cells.Lipids. 2015 Dec;50(12):1167-84. doi: 10.1007/s11745-015-4075-z. Epub 2015 Nov 5. Lipids. 2015. PMID: 26537505
-
Adipogenesis, lipogenesis and lipolysis is stimulated by mild but not severe hypoxia in 3T3-L1 cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Sep 16;478(2):727-32. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.08.015. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27498031
-
Metabolic and mind shifts: from glucose to glutamine and acetate addictions in cancer.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2015 Jul;18(4):346-53. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000178. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2015. PMID: 26001655 Review.
-
Hypoxia Dictates Metabolic Rewiring of Tumors: Implications for Chemoresistance.Cells. 2020 Dec 4;9(12):2598. doi: 10.3390/cells9122598. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33291643 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Contribution of glucose and glutamine to hypoxia-induced lipid synthesis decreases, while contribution of acetate increases, during 3T3-L1 differentiation.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 15;14(1):28193. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79458-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39548264 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle Lipid Oxidation Is Not Affected by Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Diabetes and Healthy Subjects.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 10;24(6):5308. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065308. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982383 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and mechanistic anticancer activity of new acetylated 5-aminosalicylate-thiazolinone hybrid derivatives.iScience. 2023 Dec 9;27(1):108659. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108659. eCollection 2024 Jan 19. iScience. 2023. PMID: 38235331 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

