Emerging Potential of Exosomal Non-coding RNA in Parkinson's Disease: A Review
- PMID: 35360206
- PMCID: PMC8960858
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.819836
Emerging Potential of Exosomal Non-coding RNA in Parkinson's Disease: A Review
Abstract
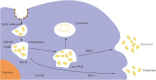
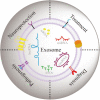
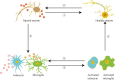
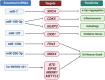
Exosomes are extracellular vesicles that are released by cells and circulate freely in body fluids. Under physiological and pathological conditions, they serve as cargo for various biological substances such as nucleotides (DNA, RNA, ncRNA), lipids, and proteins. Recently, exosomes have been revealed to have an important role in the pathophysiology of several neurodegenerative illnesses, including Parkinson's disease (PD). When secreted from damaged neurons, these exosomes are enriched in non-coding RNAs (e.g., miRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs) and display wide distribution characteristics in the brain and periphery, bridging the gap between normal neuronal function and disease pathology. However, the current status of ncRNAs carried in exosomes regulating neuroprotection and PD pathogenesis lacks a systematic summary. Therefore, this review discussed the significance of ncRNAs exosomes in maintaining the normal neuron function and their pathogenic role in PD progression. Additionally, we have emphasized the importance of ncRNAs exosomes as potential non-invasive diagnostic and screening agents for the early detection of PD. Moreover, bioengineered exosomes are proposed to be used as drug carriers for targeted delivery of RNA interference molecules across the blood-brain barrier without immune system interference. Overall, this review highlighted the diverse characteristics of ncRNA exosomes, which may aid researchers in characterizing future exosome-based biomarkers for early PD diagnosis and tailored PD medicines.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; diagnosis; exosome; non-coding RNAs; pathogenesis; treatment.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Rasheed, Liang, Wang, Feng and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exosomal noncoding RNAs in central nervous system diseases: biological functions and potential clinical applications.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Nov 9;15:1004221. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.1004221. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36438184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Roles of Exosomal Non-Coding RNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Feb 24;12:790916. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.790916. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35280805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential of exosomal biomarkers: Revolutionizing Parkinson's disease: How do they influence pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapeutic strategies?AIMS Neurosci. 2024 Sep 23;11(3):374-397. doi: 10.3934/Neuroscience.2024023. eCollection 2024. AIMS Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39431275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal microRNAs in Parkinson's disease: insights into biomarker potential and disease pathology.Neurol Sci. 2024 Aug;45(8):3625-3639. doi: 10.1007/s10072-024-07439-2. Epub 2024 Mar 27. Neurol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38532190 Review.
-
Advances in different adult stem cell-derived exosomal non-coding RNAs for the treatment of neurological disorders: a narrative review.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Oct 9;12:1459246. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1459246. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39450275 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exosome: an overview on enhanced biogenesis by small molecules.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jun;398(6):6473-6508. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03762-9. Epub 2025 Jan 25. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39862264 Review.
-
Biology, Pathology, and Targeted Therapy of Exosomal Cargoes in Parkinson's Disease: Advances and Challenges.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jul;62(7):8381-8399. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04788-7. Epub 2025 Feb 25. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39998798 Review.
-
Regulation of Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Immune Responses against Antigen-Specific Presentation.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Oct 10;10(10):1691. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10101691. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36298556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal miR-320e as a Novel Potential Biomarker for Cerebral Small Vessel Disease.Int J Gen Med. 2023 Feb 21;16:641-655. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S399338. eCollection 2023. Int J Gen Med. 2023. PMID: 36851997 Free PMC article.
-
Neurospecific Molecules Measured in Periphery in Humans: How Do They Correlate with the Brain Levels? A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 16;23(16):9193. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169193. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012459 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

