Advanced Cognitive Algorithm for Biomedical Data Processing: COVID-19 Pattern Recognition as a Case Study
- PMID: 35360478
- PMCID: PMC8964186
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1773259
Advanced Cognitive Algorithm for Biomedical Data Processing: COVID-19 Pattern Recognition as a Case Study
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Advanced Cognitive Algorithm for Biomedical Data Processing: COVID-19 Pattern Recognition as a Case Study.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Aug 9;2023:9846985. doi: 10.1155/2023/9846985. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37593466 Free PMC article.
Abstract
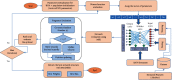
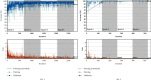
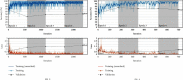
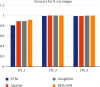
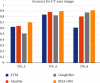
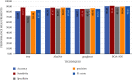
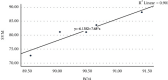
Automated disease prediction has now become a key concern in medical research due to exponential population growth. The automated disease identification framework aids physicians in diagnosing disease, which delivers accurate disease prediction that provides rapid outcomes and decreases the mortality rate. The spread of Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has a significant effect on public health and the everyday lives of individuals currently residing in more than 100 nations. Despite effective attempts to reach an appropriate trend to forecast COVID-19, the origin and mutation of the virus is a crucial obstacle in the diagnosis of the detected cases. Even so, the development of a model to forecast COVID-19 from chest X-ray (CXR) and computerized tomography (CT) images with the correct decision is critical to assist with intelligent detection. In this paper, a proposed hybrid model of the artificial neural network (ANN) with parameters optimization by the butterfly optimization algorithm has been introduced. The proposed model was compared with the pretrained AlexNet, GoogLeNet, and the SVM to identify the publicly accessible COVID-19 chest X-ray and CT images. There were six datasets for the examinations: three datasets with X-ray pictures and three with CT images. The experimental results approved the superiority of the proposed model for cognitive COVID-19 pattern recognition with average accuracy 90.48, 81.09, 86.76, and 84.97% for the proposed model, support vector machine (SVM), AlexNet, and GoogLeNet, respectively.
Copyright © 2022 Mohamed Elhoseny et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Deep Learning Algorithm for COVID-19 Classification Using Chest X-Ray Images.Comput Math Methods Med. 2021 Nov 9;2021:9269173. doi: 10.1155/2021/9269173. eCollection 2021. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021. PMID: 34795794 Free PMC article.
-
Chest X-ray image phase features for improved diagnosis of COVID-19 using convolutional neural network.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021 Feb;16(2):197-206. doi: 10.1007/s11548-020-02305-w. Epub 2021 Jan 9. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021. PMID: 33420641 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Method Diagnosis of Blood Microscopic Sample for Early Detection of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Based on Deep Learning and Hybrid Techniques.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Feb 19;22(4):1629. doi: 10.3390/s22041629. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35214531 Free PMC article.
-
Transfer learning-based ensemble support vector machine model for automated COVID-19 detection using lung computerized tomography scan data.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2021 Apr;59(4):825-839. doi: 10.1007/s11517-020-02299-2. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2021. PMID: 33738639 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-DSNet: A novel deep convolutional neural network for detection of coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) cases from CT and Chest X-Ray images.Artif Intell Med. 2022 Dec;134:102427. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2022.102427. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Artif Intell Med. 2022. PMID: 36462906 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Flexible Bayesian Parametric Proportional Hazard Model: Simulation and Applications to Right-Censored Healthcare Data.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Jun 2;2022:2051642. doi: 10.1155/2022/2051642. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. PMID: 35693888 Free PMC article.
-
An analysis of retracted COVID-19 articles published by one medical publisher with multiple journals.Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2024 Mar 5;37(3):459-464. doi: 10.1080/08998280.2024.2313333. eCollection 2024. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2024. PMID: 38628334 Free PMC article.
-
An Optimized Model Based on Deep Learning and Gated Recurrent Unit for COVID-19 Death Prediction.Biomimetics (Basel). 2023 Nov 17;8(7):552. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics8070552. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37999193 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel COVID-19 Diagnostic System Using Biosensor Incorporated Artificial Intelligence Technique.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 May 28;13(11):1886. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13111886. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37296738 Free PMC article.
-
Greylag goose optimization and multilayer perceptron for enhancing lung cancer classification.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 10;14(1):23784. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72013-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39390014 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nguyen T. T. Artificial intelligence in the battle against coronavirus (COVID-19): a survey and future research directions. 2020. https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.07343 .
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

