The Relationship Between Perfectionism and Sports Ethics Among Young Athletes Based on Achievement Goal Theory
- PMID: 35360595
- PMCID: PMC8961505
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.771332
The Relationship Between Perfectionism and Sports Ethics Among Young Athletes Based on Achievement Goal Theory
Abstract
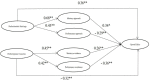
Exercise plays an important role in the process of socialization among young people and children by providing a context in which children can be exposed to the existing rules and values of society. However, the increasing news of unethical behaviors reported in competitive scenarios led the public to suspect the view "sports shape great characters." To investigate the issue and explore potential influencing factors, the study examined the relationship among athletes' perfectionism, achievement goals, and sports ethics based on the achievement goal theory. A total of 243 young athletes were recruited. The multidimensional perfectionism, achievement goals, and sports ethics were measured by a battery of questionnaires. A direct effect model that did not include mediation variables (achievement goals) and a mediation effect model that included mediation variables were analyzed by structural equation modeling (SEM). Results indicated that perfectionistic strivings may positively predict sports ethics, whereas perfectionistic concerns may negatively predict sports ethics. Mastery approach and mastery avoidance may positively predict sports ethics, whereas the performance approach and performance avoidance may negatively predict sports ethics. Achievement goals may partially mediate the relationship between perfectionism and sports ethics. Perfectionistic strivings may negatively predict sports ethics through performance approach and positively predict sports ethics through mastery approach. Perfectionistic concerns may negatively predict sports ethics through performance avoidance and positively predict sports ethics through mastery avoidance. To prevent athletes from using unethical behaviors, strategies should be developed to reduce perfectionistic concerns and increase their perfectionistic strivings.
Keywords: SEM; achievement goal; athletes; ethic; perfectionism.
Copyright © 2022 Sun and Ji.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Barkoukis V., Lazuras L., Tsorbatzoudis H., Rodafinos A. (2011). Motivational and sportspersonship profiles of elite athletes in relation to doping behavior. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 12 205–212. 10.1016/j.psychsport.2010.10.003 - DOI
-
- Chang E., Seong H., Lee S. M. (2020). Exploring the relationship between perfectionism and academic burnout through achievement goals: a mediation model. Asia Pac. Educ. Rev. 21 409–422. 10.1007/s12564-020-09633-1 - DOI
-
- Conroy D. E., Elliot A. J., Hofer S. M. (2003). A 2× 2 achievement goals questionnaire for sport: evidence for factorial invariance, temporal stability, and external validity. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 25 456–476. 10.1123/jsep.25.4.456 - DOI
-
- Corrion K., D’Arripe-Longueville F., Chalabaev A., Schiano-Lomoriello S., Roussel P., Cury F. (2010). Effect of implicit theories on judgement of cheating acceptability in physical education: the mediating role of achievement goals. J. Sports Sci. 28 909–919. 10.1080/02640414.2010.484065 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources