Prime-seq, efficient and powerful bulk RNA sequencing
- PMID: 35361256
- PMCID: PMC8969310
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-022-02660-8
Prime-seq, efficient and powerful bulk RNA sequencing
Abstract
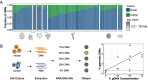
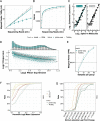
Cost-efficient library generation by early barcoding has been central in propelling single-cell RNA sequencing. Here, we optimize and validate prime-seq, an early barcoding bulk RNA-seq method. We show that it performs equivalently to TruSeq, a standard bulk RNA-seq method, but is fourfold more cost-efficient due to almost 50-fold cheaper library costs. We also validate a direct RNA isolation step, show that intronic reads are derived from RNA, and compare cost-efficiencies of available protocols. We conclude that prime-seq is currently one of the best options to set up an early barcoding bulk RNA-seq protocol from which many labs would profit.
Keywords: Genomics; Power analysis; RNA-seq; Transcriptomics.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Stark R, Grzelak M, Hadfield J. RNA sequencing: the teenage years. Nat Rev Genet. 2019;20:631–656. - PubMed
-
- Ziegenhain C, Vieth B, Parekh S, Reinius B, Guillaumet-Adkins A, Smets M, et al. Comparative analysis of single-cell RNA sequencing methods. Mol Cell. 2017;65:631–43.e4. - PubMed
-
- Svensson V, Vento-Tormo R, Teichmann SA. Exponential scaling of single-cell RNA-seq in the past decade. Nat Protoc. 2018;13:599–604. - PubMed
-
- Mereu E, Lafzi A, Moutinho C, Ziegenhain C, McCarthy DJ, Álvarez-Varela A, et al. Benchmarking single-cell RNA-sequencing protocols for cell atlas projects. Nat Biotechnol. 2020;38:747–755. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

