Study on the role of transcription factor SPI1 in the development of glioma
- PMID: 35361282
- PMCID: PMC8973577
- DOI: 10.1186/s41016-022-00276-2
Study on the role of transcription factor SPI1 in the development of glioma
Abstract
Background: Glioma is a common malignant brain tumor. The purpose of this study was to investigate the role of the transcription factor SPI1 in glioma.
Methods: SPI1 expression in glioma was identified using qRT-PCR and Western blotting. Cell proliferation was assessed using the CCK8 assay. Transwell and wound healing assays were utilized to evaluate cell migration. Additionally, cell cycle and apoptosis were detected using flow cytometry.
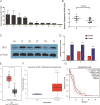
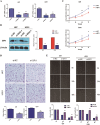
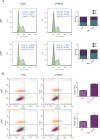
Results: We observed that the expression level of SPI1 was up-regulated in glioma tissues, compared to normal tissues. Furthermore, we found that SPI1 is able to promote proliferation and migration of glioma cells in vitro. Flow cytometry results demonstrate that, compared to si-NC cells, si-SPI1 cells stagnated in the G1 phase, and down-regulation of SPI1 expression is able to increase rates of apoptosis. Double luciferase activity and chromatin immunoprecipitation assay results indicated that SPI1 can bind to the promoter sites and promote the proliferation and migration of glioma cells by regulating the expression of oncogenic PAICS.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that SPI1 can promote proliferation and migration of glioma. Furthermore, SPI1 can be utilized as a potential diagnostic marker and therapeutic target for glioma.
Keywords: Glioma; PAICS; SPI1; migration; proliferation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Guo WQ, Chen YG, Shi RZ, He K, Wang JF, Shao JH, et al. 20(S)-Protopanaxdiol Suppresses the Abnormal Granule-Monocyte Differentiation of Hematopoietic Stem Cells in 4T1 Breast Cancer-Bearing Mouse. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:8747023. doi: 10.1155/2020/8747023. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
