Synergistic activation of the insulin receptor via two distinct sites
- PMID: 35361965
- PMCID: PMC9115778
- DOI: 10.1038/s41594-022-00750-6
Synergistic activation of the insulin receptor via two distinct sites
Abstract
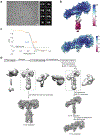
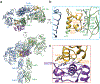
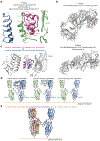
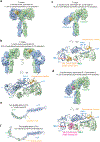
Insulin receptor (IR) signaling controls multiple facets of animal physiology. Maximally four insulins bind to IR at two distinct sites, termed site-1 and site-2. However, the precise functional roles of each binding event during IR activation remain unresolved. Here, we showed that IR incompletely saturated with insulin predominantly forms an asymmetric conformation and exhibits partial activation. IR with one insulin bound adopts a Γ-shaped conformation. IR with two insulins bound assumes a Ƭ-shaped conformation. One insulin binds at site-1 and another simultaneously contacts both site-1 and site-2 in the Ƭ-shaped IR dimer. We further show that concurrent binding of four insulins to sites-1 and -2 prevents the formation of asymmetric IR and promotes the T-shaped symmetric, fully active state. Collectively, our results demonstrate how the synergistic binding of multiple insulins promotes optimal IR activation.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures













References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

