Development and Application of an Open Tool for Sharing and Analyzing Integrated Clinical and Environmental Exposures Data: Asthma Use Case
- PMID: 35363149
- PMCID: PMC9015759
- DOI: 10.2196/32357
Development and Application of an Open Tool for Sharing and Analyzing Integrated Clinical and Environmental Exposures Data: Asthma Use Case
Abstract
Background: The Integrated Clinical and Environmental Exposures Service (ICEES) serves as an open-source, disease-agnostic, regulatory-compliant framework and approach for openly exposing and exploring clinical data that have been integrated at the patient level with a variety of environmental exposures data. ICEES is equipped with tools to support basic statistical exploration of the integrated data in a completely open manner.
Objective: This study aims to further develop and apply ICEES as a novel tool for openly exposing and exploring integrated clinical and environmental data. We focus on an asthma use case.
Methods: We queried the ICEES open application programming interface (OpenAPI) using a functionality that supports chi-square tests between feature variables and a primary outcome measure, with a Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons (α=.001). We focused on 2 primary outcomes that are indicative of asthma exacerbations: annual emergency department (ED) or inpatient visits for respiratory issues; and annual prescriptions for prednisone.
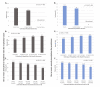
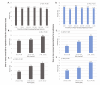
Results: Of the 157,410 patients within the asthma cohort, 26,332 (16.73%) had 1 or more annual ED or inpatient visits for respiratory issues, and 17,056 (10.84%) had 1 or more annual prescriptions for prednisone. We found that close proximity to a major roadway or highway, exposure to high levels of particulate matter ≤2.5 μm (PM2.5) or ozone, female sex, Caucasian race, low residential density, lack of health insurance, and low household income were significantly associated with asthma exacerbations (P<.001). Asthma exacerbations did not vary by rural versus urban residence. Moreover, the results were largely consistent across outcome measures.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that the open-source ICEES can be used to replicate and extend published findings on factors that influence asthma exacerbations. As a disease-agnostic, open-source approach for integrating, exposing, and exploring patient-level clinical and environmental exposures data, we believe that ICEES will have broad adoption by other institutions and application in environmental health and other biomedical fields.
Keywords: airborne pollutant exposures; asthma exacerbation; electronic health records; medication exposures; open patient data; socioeconomic exposures.
©Karamarie Fecho, Stanley C Ahalt, Stephen Appold, Saravanan Arunachalam, Emily Pfaff, Lisa Stillwell, Alejandro Valencia, Hao Xu, David B Peden. Originally published in JMIR Formative Research (https://formative.jmir.org), 01.04.2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: DBP receives funding from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences; the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; the US Environmental Protection Agency; and the US Department of Defense. He has been a consultant for GlaxoSmithKline, Teva, and Sanofi. All other authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Biomedical Data Translator Consortium The Biomedical Data Translator program: conception, culture, and community. Clin Transl Sci. 2019 Mar;12(2):91–94. doi: 10.1111/cts.12592. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/30412340 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Biomedical Data Translator Consortium Toward a universal biomedical data translator. Clin Transl Sci. 2019 Mar;12(2):86–90. doi: 10.1111/cts.12591. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/30412337 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fecho K, Pfaff E, Xu H, Champion J, Cox S, Stillwell L, Peden David B, Bizon Chris, Krishnamurthy A, Tropsha A, Ahalt S. A novel approach for exposing and sharing clinical data: the Translator Integrated Clinical and Environmental Exposures Service. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2019 Oct 01;26(10):1064–1073. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocz042. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/31077269 5480568 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

