The prognostic role of combining Krüppel-like factor 4 score and grade of inflammation in a Norwegian cohort of oral tongue squamous cell carcinomas
- PMID: 35363406
- PMCID: PMC9321830
- DOI: 10.1111/eos.12866
The prognostic role of combining Krüppel-like factor 4 score and grade of inflammation in a Norwegian cohort of oral tongue squamous cell carcinomas
Abstract
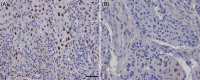
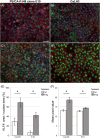
Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) is a zinc-finger transcription factor involved in inflammation, cancer development, and progression. However, the relationship between KLF4, inflammation, and prognosis in oral cancer is not fully understood. KLF4 expression levels were examined in a multicenter cohort of 128 oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) specimens from the tongue (OTSCC) using immunohistochemistry. In two external KLF4 mRNA datasets (The Cancer Genome Atlas/The Genotype-Tissue Expression Portal), lower KLF4 mRNA expression was found in OSCC and head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCC) than in control oral epithelium. These data indicate that down-regulation of KLF4 mRNA is linked to OSCC/HNSCC progression. Using Cox-multivariate analysis, a significantly favorable 5-year disease-specific survival rate was observed for a subgroup of patients with a combination of high levels of KLF4 expression and inflammation. OSCC cell lines exposed to IFN-γ showed a significant upregulation of nuclear KLF4 expression, indicating a link between inflammation and KLF4 expression in OSCC. Overall, the current data suggest a functional link between KLF4 and inflammation. The combination of high KLF4 nuclear expression and marked/moderate stromal inflammation might be useful as a favorable prognostic marker for a subgroup of OTSCC patients.
Keywords: KLF4; cancer of the tongue; stromal cells; survival.
© 2022 The Authors. European Journal of Oral Sciences published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Scandinavian Division of the International Association for Dental Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
The study was approved by the Northern Norwegian Regional Committee for Medical Research Ethics (REK Nord; 2013/1786 and 2015/1381).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Quantitative analysis of KLF4 and SOX2 expression in oral carcinomas reveals independent association with oral tongue subsite location and histological grade.Cancer Biomark. 2021;32(1):37-48. doi: 10.3233/CBM-203086. Cancer Biomark. 2021. PMID: 34092609
-
Cortactin expression in a Norwegian cohort of human papilloma virus negative oral squamous cell carcinomas of the mobile tongue.Eur J Oral Sci. 2023 Apr;131(2):e12925. doi: 10.1111/eos.12925. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Eur J Oral Sci. 2023. PMID: 36790139
-
Oral-specific ablation of Klf4 disrupts epithelial terminal differentiation and increases premalignant lesions and carcinomas upon chemical carcinogenesis.J Oral Pathol Med. 2015 Nov;44(10):801-9. doi: 10.1111/jop.12307. Epub 2015 Jan 21. J Oral Pathol Med. 2015. PMID: 25605610
-
The Janus-faced roles of Krüppel-like factor 4 in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 29;6(42):44480-94. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6256. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26517087 Free PMC article.
-
Oral cavity cancer in young, non-smoking, and non-drinking patients: A contemporary review.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2023 Oct;190:104112. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2023.104112. Epub 2023 Aug 24. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2023. PMID: 37633348 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of stem cell markers SALL4, LIN28A, and KLF4 in ameloblastoma.Diagn Pathol. 2023 Aug 9;18(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s13000-023-01379-9. Diagn Pathol. 2023. PMID: 37559082 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring animal models in oral cancer research and clinical intervention: A critical review.Vet Med Sci. 2023 Jul;9(4):1833-1847. doi: 10.1002/vms3.1161. Epub 2023 May 17. Vet Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37196179 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

