Study protocol: MyoFit46-the cardiac sub-study of the MRC National Survey of Health and Development
- PMID: 35365075
- PMCID: PMC8972905
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-022-02582-0
Study protocol: MyoFit46-the cardiac sub-study of the MRC National Survey of Health and Development
Abstract
Background: The life course accumulation of overt and subclinical myocardial dysfunction contributes to older age mortality, frailty, disability and loss of independence. The Medical Research Council National Survey of Health and Development (NSHD) is the world's longest running continued surveillance birth cohort providing a unique opportunity to understand life course determinants of myocardial dysfunction as part of MyoFit46-the cardiac sub-study of the NSHD.
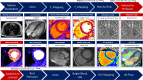
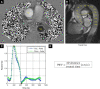
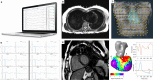
Methods: We aim to recruit 550 NSHD participants of approximately 75 years+ to undertake high-density surface electrocardiographic imaging (ECGI) and stress perfusion cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR). Through comprehensive myocardial tissue characterization and 4-dimensional flow we hope to better understand the burden of clinical and subclinical cardiovascular disease. Supercomputers will be used to combine the multi-scale ECGI and CMR datasets per participant. Rarely available, prospectively collected whole-of-life data on exposures, traditional risk factors and multimorbidity will be studied to identify risk trajectories, critical change periods, mediators and cumulative impacts on the myocardium.
Discussion: By combining well curated, prospectively acquired longitudinal data of the NSHD with novel CMR-ECGI data and sharing these results and associated pipelines with the CMR community, MyoFit46 seeks to transform our understanding of how early, mid and later-life risk factor trajectories interact to determine the state of cardiovascular health in older age.
Trial registration: Prospectively registered on ClinicalTrials.gov with trial ID: 19/LO/1774 Multimorbidity Life-Course Approach to Myocardial Health- A Cardiac Sub-Study of the MCRC National Survey of Health and Development (NSHD).
Keywords: 4-dimensional flow; Cardiovascular health; Cardiovascular magnetic resonance; Electrocardiographic imaging; Life course risk factors; Myocardial tissue characterization; Perfusion; Risk trajectories; Subclinical myocardial dysfunction.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing of interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

