Blockade of PD-L1/PD-1 signaling promotes osteo-/odontogenic differentiation through Ras activation
- PMID: 35365595
- PMCID: PMC8976080
- DOI: 10.1038/s41368-022-00168-2
Blockade of PD-L1/PD-1 signaling promotes osteo-/odontogenic differentiation through Ras activation
Abstract
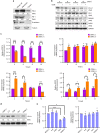
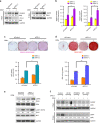
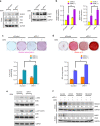
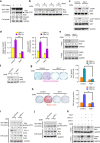
The programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) and its receptor programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) deliver inhibitory signals to regulate immunological tolerance during immune-mediated diseases. However, the role of PD-1 signaling and its blockade effect on human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs) differentiation into the osteo-/odontogenic lineage remain unknown. We show here that PD-L1 expression, but not PD-1, is downregulated during osteo-/odontogenic differentiation of hDPSCs. Importantly, PD-L1/PD-1 signaling has been shown to negatively regulate the osteo-/odontogenic differentiation of hDPSCs. Mechanistically, depletion of either PD-L1 or PD-1 expression increased ERK and AKT phosphorylation levels through the upregulation of Ras enzyme activity, which plays a pivotal role during hDPSCs osteo-/odontogenic differentiation. Treatment with nivolumab (a human anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody), which targets PD-1 to prevent PD-L1 binding, successfully enhanced osteo-/odontogenic differentiation of hDPSCs through enhanced Ras activity-mediated phosphorylation of ERK and AKT. Our findings underscore that downregulation of PD-L1 expression accompanies during osteo-/odontogenic differentiation, and hDPSCs-intrinsic PD-1 signaling inhibits osteo-/odontogenic differentiation. These findings provide a significant basis that PD-1 blockade could be effective immunotherapeutic strategies in hDPSCs-mediated dental pulp regeneration.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Zhang W, Walboomers XF, Shi S, Fan M, Jansen JA. Multilineage differentiation potential of stem cells derived from human dental pulp after cryopreservation. Tissue Eng. 2006;12:2813–2823. - PubMed
-
- Gronthos S, et al. Stem cell properties of human dental pulp stem cells. J. Dent. Res. 2002;81:531–535. - PubMed
-
- Batouli S, et al. Comparison of stem-cell-mediated osteogenesis and dentinogenesis. J. Dent. Res. 2003;82:976–981. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

