The learning curve in bladder MRI using VI-RADS assessment score during an interactive dedicated training program
- PMID: 35366122
- PMCID: PMC8976109
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-022-08766-8
The learning curve in bladder MRI using VI-RADS assessment score during an interactive dedicated training program
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of the study was to evaluate the effect of an interactive training program on the learning curve of radiology residents for bladder MRI interpretation using the VI-RADS score.
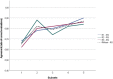
Methods: Three radiology residents with minimal experience in bladder MRI served as readers. They blindly evaluated 200 studies divided into 4 subsets of 50 cases over a 3-month period. After 2 months, the first subset was reassessed, resulting in a total of 250 evaluations. An interactive training program was provided and included educational lessons and case-based practice. The learning curve was constructed by plotting mean agreement as the ratio of correct evaluations per batch. Inter-reader agreement and diagnostic performance analysis were performed with kappa statistics and ROC analysis.
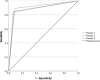
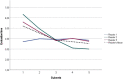
Results: As for the VI-RADS scoring agreement, the kappa differences between pre-training and post-training evaluation of the same group of cases were 0.555 to 0.852 for reader 1, 0.522 to 0.695 for reader 2, and 0.481 to 0.794 for reader 3. Using VI-RADS ≥ 3 as cut-off for muscle invasion, sensitivity ranged from 84 to 89% and specificity from 91 to 94%, while the AUCs from 0.89 (95% CI:0.84, 0.94) to 0.90 (95% CI:0.86, 0.95). Mean evaluation time decreased from 5.21 ± 1.12 to 3.52 ± 0.69 min in subsets 1 and 5. Mean grade of confidence improved from 3.31 ± 0.93 to 4.21 ± 0.69, in subsets 1 and 5.
Conclusion: An interactive dedicated education program on bladder MRI and the VI-RADS score led to a significant increase in readers' diagnostic performance over time, with a general improvement observed after 100-150 cases.
Key points: • After the first educational lesson and 100 cases were interpreted, the concordance on VI-RADS scoring between the residents and the experienced radiologist was significantly higher. • An increase in the grade of confidence was experienced after 100 cases. • We found a decrease in the evaluation time after 150 cases.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; Internship and residency; Learning curve; Magnetic resonance imaging; Training program.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Figures



References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RS, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68:394–424. 10.3322/caac.21492 - PubMed
-
- Metwally MI, Zeed NA, Hamed EM et al (2021) The validity, reliability, and reviewer acceptance of VI-RADS in assessing muscle invasion by bladder cancer: a multicenter prospective study. Eur Radiol. 10.1007/s00330-021-07765-5 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

