Hierarchical intrinsically motivated agent planning behavior with dreaming in grid environments
- PMID: 35366128
- PMCID: PMC8976870
- DOI: 10.1186/s40708-022-00156-6
Hierarchical intrinsically motivated agent planning behavior with dreaming in grid environments
Abstract
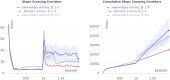
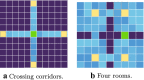
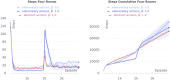
Biologically plausible models of learning may provide a crucial insight for building autonomous intelligent agents capable of performing a wide range of tasks. In this work, we propose a hierarchical model of an agent operating in an unfamiliar environment driven by a reinforcement signal. We use temporal memory to learn sparse distributed representation of state-actions and the basal ganglia model to learn effective action policy on different levels of abstraction. The learned model of the environment is utilized to generate an intrinsic motivation signal, which drives the agent in the absence of the extrinsic signal, and through acting in imagination, which we call dreaming. We demonstrate that the proposed architecture enables an agent to effectively reach goals in grid environments.
Keywords: Hierarchical temporal memory; Intrinsic motivation; Model-based reinforcement learning; Sparse distributed representations.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures







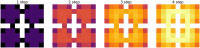








References
-
- Ahmad S, Hawkins J (2015) Properties of sparse distributed representations and their application to hierarchical temporal memory. arXiv: 1503.07469
-
- Andrychowicz M, Wolski F, Ray A, Schneider J, Fong R, Welinder P, McGrew B, Tobin J, Pieter Abbeel O, Zaremba W (2017) Hindsight experience replay. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, 30
-
- Antonio Becerra J, Romero A, Bellas F, Duro RJ. Motivational engine and long-term memory coupling within a cognitive architecture for lifelong open-ended learning. Neurocomputing. 2021;452:341–354. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.10.124. - DOI
-
- Asada M, MacDorman KF, Ishiguro H, Kuniyoshi Y. Cognitive developmental robotics as a new paradigm for the design of humanoid robots. Robot Auton Syst. 2001;37(2–3):185–193. doi: 10.1016/S0921-8890(01)00157-9. - DOI
-
- Bacon P-L, Harb J, Precup D (2017) The option-critic architecture. In: Proceedings of the thirty-first AAAI conference on artificial intelligence. AAAI’17, AAAI Press, pp 1726–34
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

