Anterior segment structures in dark iris Chinese patients with unilateral Fuchs' uveitis syndrome
- PMID: 35366140
- PMCID: PMC9420092
- DOI: 10.1007/s10792-022-02282-w
Anterior segment structures in dark iris Chinese patients with unilateral Fuchs' uveitis syndrome
Abstract
Purpose: To compare binocular anterior segment structures in Chinese patients with dark iris and unilateral Fuchs' uveitis syndrome (FUS).
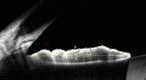
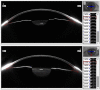
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study including 34 phakic eyes (17 patients) with unilateral FUS. Anterior segment parameters were measured by rotating Scheimpflug imaging camera, noncontact specular microscopy, and anterior segment optical coherence tomography.
Results: Corneal volume was higher in FUS eyes compared to unaffected eyes (p < 0.05). The iridocorneal angles were larger in FUS eyes compared to contralateral eyes (p < 0.05). Mean endothelial cell density (ECD) was lower, and the coefficient of variation in endothelial cell size and average cell area of endothelial cells (ACA) were higher, in FUS eyes (p < 0.05). Mean densitometry values of the midstromal cornea (zones with a diameter of 0-2, 2-6, or 10-12 mm), posterior (0-2, 2-6, 10-12, or 0-12 mm), or total thickness (0-2 or 2-6 mm) were higher in FUS eyes compared with unaffected eyes (p < 0.05). ECD, percentage of hexagonal cells, and ACA were strongly related to densitometry values of the midstromal and posterior cornea in the FUS eyes (p < 0.05). Smoothness index of iris was lager in affected eyes (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: In Chinese patients with unilateral FUS, loss of endothelial cells, wider iridocorneal angle, thicker cornea, higher corneal densitometry of midstromal and posterior layer, and smoother iris were observed in affected eyes compared to contralateral eyes. These data can help to elucidate anterior segment characteristics of unilateral FUS in this population.
Keywords: Anterior segment structure; Chinese patients; Dark iris; Fuchs; Uveitis syndrome.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fuchs E. Uber Komplicationen der Heterochromie. Z Augenheilk. 1906;15:191–212.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

