Diacerein ameliorates acetaminophen hepatotoxicity in rats via inhibiting HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB and upregulating PPAR-γ signal
- PMID: 35366176
- PMCID: PMC8975726
- DOI: 10.1007/s11033-022-07366-5
Diacerein ameliorates acetaminophen hepatotoxicity in rats via inhibiting HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB and upregulating PPAR-γ signal
Abstract
Background: Acetaminophen (APAP) is a worldwide antipyretic as well as an analgesic medication. It has been extensively utilized during the outbreak of coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19). APAP misuse would lead to liver injury. Diacerein (DIA), an anthraquinone derivative, has antioxidant and inflammatory properties. Hence, this study attempted to evaluate the impact of DIA treatment on liver injury induced by APAP and its influence on nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) /toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/high mobility group box-1(HMGB-1) signaling as well as the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPAR-γ) expression.
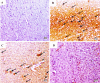
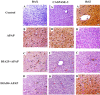
Methods: Male albino rats received 25 as well as 50 mg/kg/day DIA orally for seven days. One hour after the last administration, rats received APAP (1gm/kg, orally). For histopathological analysis, liver tissues and blood were collected, immunohistochemical (IHC) assay, biochemical assay, as well as quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR).
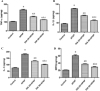
Results: DIA markedly reduced liver injury markers and ameliorated histopathological changes. Moreover, DIA dose-dependently alleviated oxidative stress status caused by APAP administration along with inflammatory markers, including the level of interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), myeloperoxidase (MPO), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and interleukin 6 (IL-6). Furthermore, DIA downregulated protein levels as well as mRNA of HMGB-1, TLR4, NF-κB p65 expression, and enhanced PPAR-γ expression. Moreover, DIA ameliorated apoptotic (Bax) and caspase-3 expressions and increased the anti-apoptotic (Bcl2) expression.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated that DIA exerts anti-apoptotic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties against liver injury induced by APAP that is attributed to inhibition of the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB pathway, besides upregulation of the expression of PPAR-γ.
Keywords: Acetaminophen (APAP); Bax/Bcl2/caspase-3; Diacerein (DIA); HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB signaling; Hepatotoxicity; PPAR-γ.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest to declare.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

