Systemic Action of Inflammatory Mediators in Patients with Essential Hypertension and Diastolic Chronic Heart Failure: A Clinical Pathophysiological Study
- PMID: 35366254
- PMCID: PMC8830453
- DOI: 10.3390/pathophysiology27010005
Systemic Action of Inflammatory Mediators in Patients with Essential Hypertension and Diastolic Chronic Heart Failure: A Clinical Pathophysiological Study
Abstract
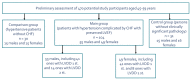
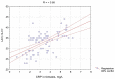
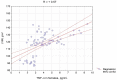
The aim of this research was to correlate indicators of proinflammatory status and the structural/functional characteristics of the cardiovascular system comparatively in male and female patients with essential hypertension (EH) complicated by diastolic chronic heart failure (CHF) with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). The study included 104 middle-aged patients (55 males (M) and 49 females (F)) with first- or second-degree EH complicated by CHF with preserved LVEF. They all belonged to the low functional class of CHF, with LVEF ≥50%, first- or second-degree of LV diastolic dysfunction (LVDD), LV hypertrophy (LVH), and dilatation of the left atrium (LA) with a sinus rhythm and N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide >125 pg/mL. Serum levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) were measured. To identify the relationship between the proinflammatory pattern and cardiovascular parameters, Spearman's rank correlation coefficients were determined. M had markedly higher levels of CRP, TNF-α, and IL-6 compared to F. However, all the mean values corresponded to the reference range. Significant direct associations of CRP level with the LV mass index (LVMI), relative wall thickness (RWT), LA volume index (LAVI), E/e' ratio, and systolic and diastolic blood pressure (SBP, DBP) existed in both M and F, as well as negative correlations of CRP with LVDD parameter e' and distance covered in a 6 min walk test. M and F had a positive association between IL-6 and LVMI, LAVI, E/e' ratio, SBP, RWT, and DBP, as well as strong negative associations between IL-6 and e' and distance passed in 6 min in each group. Significant direct correlations existed between serum TNF-α level and LVMI, RWT, LAVI, E/e', SBP, and DBP both in M and F. Furthermore, there were negative relationships of TNF-α level with e' and the distance covered for the 6 min walk. This study demonstrated a close relationship between the blood levels of proinflammatory autacoids and indicators of EH, exercise tolerance, LVH, LVDD, and LA enlargement, regardless of the patient's sex. Compared to female patients, male patients had stronger correlations of CRP, TNF-α, and IL-6 levels with indicators of LVDD degree.
Keywords: chronic heart failure; correlation analysis; diastolic dysfunction; essential hypertension; preserved ejection fraction; proinflammatory status; sex differences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Stroev Y.I., Kaminova O.M., Serdyuk I.Y., Nitsa N.A., Chesnokov L.P., Churilov L.P. Immunoendocrine interactions in acute and chronic diseases as a manifestation of typical conflict between systemic and local regulation [in Russian] Tavricheskiy Med.-Biol. Vestnik. 2012;15:230–232.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
