Chitosan from Crabs (Scylla serrata) Represses Hyperlipidemia-Induced Hepato-Renal Dysfunctions in Rats: Modulation of CD43 and p53 Expression
- PMID: 35366259
- PMCID: PMC8830478
- DOI: 10.3390/pathophysiology28020015
Chitosan from Crabs (Scylla serrata) Represses Hyperlipidemia-Induced Hepato-Renal Dysfunctions in Rats: Modulation of CD43 and p53 Expression
Abstract
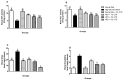
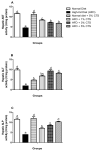
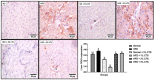
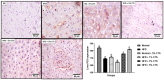
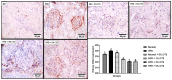
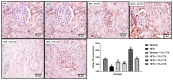
Hepato-renal dysfunctions associated with hyperlipidemia necessitates a continuous search for natural remedies. This study thus evaluated the effect of dietary chitosan on diet-induced hyperlipidemia in rats. A total of 30 male Wistar rats (90 ± 10) g were randomly allotted into six (6) groups (n = 5): Normal diet, High-fat diet (HFD), and Normal diet + 5% chitosan. The three other groups received HFD, supplemented with 1%, 3%, and 5% of chitosan. The feeding lasted for 6 weeks, after which the rats were sacrificed. The liver and kidneys were harvested for analyses. Hepatic alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity, and renal biomarkers (ALT, AST, urea, and creatinine) were assayed spectrophotometrically. Additionally, expression of hepatic and renal CD43 and p53 was estimated immunohistochemically. The HFD group had elevated bodyweight compared to normal which was reversed in the chitosan-supplemented groups. Hyperlipidemia caused a significant (p < 0.05) decrease in the hepatic (AST, ALT, and ALP) and renal (AST and ALT) activities, while renal urea and creatinine increased. Furthermore, the HFD group showed an elevated level of hepatic and renal CD43 while p53 expression decreased. However, groups supplemented with chitosan showed improved hepatic and renal biomarkers, as well as corrected the aberrations in the expressions of p53 and CD43. Conclusively, dietary chitosan inclusion in the diet (between 3% and 5%) could effectively improve kidney and liver functionality via abatement of inflammatory responses.
Keywords: chitosan; functional indices; high-fat diet; hyperlipidemia; p53 and CD43 genes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ugbaja R.N., Akinloye D.I., James A.S., Ugwor E.I., Kareem S.E., David G., Abolade S.O., Oyebade O.E. Crab derived dietary chitosan mollifies hyperlipidemia- induced oxidative stress and histopathological Derangements in male albino rats. Obes. Med. 2020;20:100300. doi: 10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100300. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
