Coenzyme Q10 and Silymarin Reduce CCl4-Induced Oxidative Stress and Liver and Kidney Injury in Ovariectomized Rats-Implications for Protective Therapy in Chronic Liver and Kidney Diseases
- PMID: 35366269
- PMCID: PMC8830449
- DOI: 10.3390/pathophysiology28010005
Coenzyme Q10 and Silymarin Reduce CCl4-Induced Oxidative Stress and Liver and Kidney Injury in Ovariectomized Rats-Implications for Protective Therapy in Chronic Liver and Kidney Diseases
Abstract
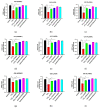
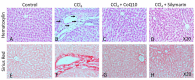
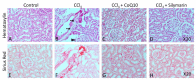
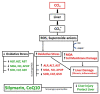
Oxidative stress is one of the key factors in the pathophysiology of liver disease. The present study aimed to evaluate the potential impact of two antioxidants, namely coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) and silymarin, on carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced oxidative stress and hepatic damage in ovariectomized rats. Female Long Evans rats were divided into six groups (n = 6): control, CCl4, CCl4 + CoQ10 (200 mg/kg), CCl4 + silymarin (140 mg/kg), Control + CoQ10, and Control + silymarin. Plasma and tissues from liver and kidney were analyzed for oxidative stress parameters and antioxidant enzyme activities using biochemical assays. Infiltration of inflammatory cells and fibrosis were assessed by histological staining of tissue sections. Both CoQ10 and silymarin significantly lowered serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels that were detected to be higher in CCl4 rats compared to controls. Significant reduction in CCl4-induced elevated levels of oxidative stress markers malondialdehyde (MDA), nitric oxide (NO), and advanced protein oxidation product (APOP) was observed with both antioxidants. However, in control rats, CoQ10 and silymarin did not produce a significant effect. Histological analysis revealed that CCl4 markedly increased the level of inflammatory cells infiltration and fibrosis in liver and kidney tissues, but this was significantly reduced in CCl4 + CoQ10 and CCl4 + silymarin groups. Taken together, our results suggest that CoQ10 and silymarin can protect the liver against oxidative damage through improved antioxidant enzyme activities and reduced lipid peroxidation. Thus, supplementation of the aforementioned antioxidants may be useful as a therapeutic intervention to protect liver health in chronic liver diseases.
Keywords: CCl4; coenzyme Q10; ovariectomized rat model; oxidative stress; silymarin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Astaxanthin Ameliorates Hepatic Damage and Oxidative Stress in Carbon Tetrachloride-administered Rats.Pharmacognosy Res. 2017 Dec;9(Suppl 1):S84-S91. doi: 10.4103/pr.pr_26_17. Pharmacognosy Res. 2017. PMID: 29333048 Free PMC article.
-
Apocynin prevented inflammation and oxidative stress in carbon tetra chloride induced hepatic dysfunction in rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Aug;92:421-428. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.05.101. Epub 2017 May 27. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28558355
-
Supplementation of fresh ucche (Momordica charantia L. var. muricata Willd) prevented oxidative stress, fibrosis and hepatic damage in CCl4 treated rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 Apr 11;15:115. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0636-1. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015. PMID: 25884170 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on liver enzymes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Jun 7;11(9):4912-4925. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3478. eCollection 2023 Sep. Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37701221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coenzyme Q10 and Its Therapeutic Potencies Against COVID-19 and Other Similar Infections: A Molecular Review.Adv Pharm Bull. 2023 Mar;13(2):233-243. doi: 10.34172/apb.2023.026. Epub 2021 Nov 7. Adv Pharm Bull. 2023. PMID: 37342382 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Amelioration of CCl4-induced oxidative stress and hepatotoxicity by Ganoderma lucidum in long evans rats.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 19;13(1):9909. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-35228-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37336915 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Silymarin in Mitigating Paclitaxel-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity: Insights into Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in Rats.Balkan Med J. 2024 May 3;41(3):193-205. doi: 10.4274/balkanmedj.galenos.2024.2024-1-60. Balkan Med J. 2024. PMID: 38700358 Free PMC article.
-
Dimethyl fumarate effects on paraquat-induced hepatotoxicity in mice via anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic activities.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 31;15(1):3897. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88461-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39890857 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potentials of Colocasia affinis Leaf Extract for the Alleviation of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes and Diabetic Complications: In vivo and in silico-Based Studies.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Feb 19;14:443-459. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S297348. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 33642871 Free PMC article.
-
Coenzyme Q10 ameliorates carbofuran induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in wister rats.Heliyon. 2023 Feb 14;9(2):e13727. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13727. eCollection 2023 Feb. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36865458 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bae J.H.A., Lee S.H., Kim H.J., Lee J.Y. The Role of Salicornia herbacea in Ovariectomy-Induced Oxidative Stress. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006;29:1305–1309. - PubMed
-
- Jain P., Haque A., Islam T., Alam M.A., Reza H.M. Comparative evaluation of Ziziphus mauritiana leaf extracts for phenolic content, antioxidant and antibacterial activities. J. Herbs Spices Med. Plants. 2019;25:236–258. doi: 10.1080/10496475.2019.1600627. - DOI
-
- Adebayo A.H., Yakubu O.F., Balogun T.M. Protective properties of Citrullus lanatus on carbon tetrachloride induced liver damage in rats. Eur. J. Med. Plants. 2014;4:979–989. doi: 10.9734/EJMP/2014/9690. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
