Amyloid Beta Peptides and Th1 Cytokines Modulate Human Brain Vascular Smooth Muscle Tonic Contractile Capacity In Vitro: Relevance to Alzheimer's Disease?
- PMID: 35366270
- PMCID: PMC8830442
- DOI: 10.3390/pathophysiology28010006
Amyloid Beta Peptides and Th1 Cytokines Modulate Human Brain Vascular Smooth Muscle Tonic Contractile Capacity In Vitro: Relevance to Alzheimer's Disease?
Abstract
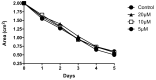
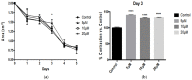
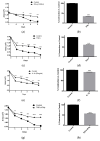
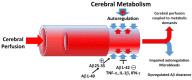
Alzheimer's Disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative condition characterized both by the presence of tau protein neurofibrillary tangles and amyloid beta (Aβ) containing extracellular "plaques". The cleavage of amyloid precursor protein (APP) yields several Aβ peptides. Although Aβ toxicity to neurons has been described extensively, its effects on other components of the neurovasculature such as vascular smooth muscle cells have been less well characterized. AD is now also recognized as a neurovascular disease characterized by cerebral microbleeds and disturbances in autoregulation. AD is also a neuroinflammatory condition in which several proinflammatory cytokines are elevated and may contribute to the intensification of AD severity. Cerebral autoregulation (the mechanism by which brain blood flow is maintained despite changes in perfusion pressure) is extremely tightly controlled in the brain and shows disturbances in AD. The failure of autoregulation in AD may make the brain susceptible to cerebral microbleeds through a reduced capacity to limit blood flow when pressure is increased. Conversely, reduced vasodilation during low flow might could also exacerbate tissue hypoxia. Currently, whether and how Aβ peptides and inflammatory cytokines depress brain smooth muscle cell tonic contraction is not known, but could reveal important targets in the preservation of autoregulation which is disturbed in AD. We used a collagen gel contractility assay to evaluate the influence of Aβ25-35, Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 peptides and inflammatory cytokines on the tonic contractility of human brain vascular smooth muscle cells (HBVSMC) as an in vitro model of cerebral autoregulation. We found that 5 and 10 μM Aβ1-42 significantly depressed HBVSM contractility, while Aβ1-40 5-20 μM had no effect on contractility. Conversely, Aβ25-35 (1-50 μM) increased contractility. Interestingly, the inflammatory cytokines TNF-α (20 ng/mL), IL-1β (20 ng/mL) and IFN-γ (1000 U/mL) also depressed HBVSM tonic contractility alone and in combination. These data suggest that both the inflammatory milieu in AD as well as the abundance of Aβ peptides may promote autoregulatory failure and increase brain susceptibility to dysregulated perfusion and microbleeds which are an important and devastating characteristic of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; inflammatory cytokine; tonic contraction; vascular smooth muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Liao Y.-F., Wang B.-J., Cheng H.-T., Kuo L.-H., Wolfe M.S. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α, Interleukin-1β, and Interferon-γ Stimulate γ-Secretase-mediated Cleavage of Amyloid Precursor Protein through a JNK-dependent MAPK Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:49523–49532. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M402034200. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
