Moringa oleifera Extract Extenuates Echis ocellatus Venom-Induced Toxicities, Histopathological Impairments and Inflammation via Enhancement of Nrf2 Expression in Rats
- PMID: 35366273
- PMCID: PMC8830474
- DOI: 10.3390/pathophysiology28010009
Moringa oleifera Extract Extenuates Echis ocellatus Venom-Induced Toxicities, Histopathological Impairments and Inflammation via Enhancement of Nrf2 Expression in Rats
Abstract
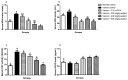
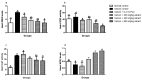
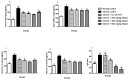
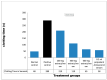
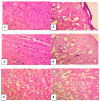
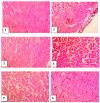
Echis ocellatus snakebite causes more fatalities than all other African snake species combined. Moringa oleifera reportedly possesses an antivenom property. Therefore, we evaluated the effectiveness of M. oleifera ethanol extract (MOE) against E. ocellatus venom (EOV) toxicities. Thirty male rats were grouped as follows (n = 5): Group 1 (normal control received saline), groups 2 to 6 were administered intraperitoneally, 0.22 mg/kg (LD50) of EOV. Group 2 was left untreated while group 3 to 6 were treated post-envenoming with 0.2 mL of polyvalent antivenom, 200, 400, and 600 mg/kg of MOE respectively. MOE significantly (p < 0.05) normalized the altered haematological indices and blood electrolytes profiles. MOE attenuated venom-induced cellular dysfunctions, characterized by a significant increase in NRF2, and concomitant downregulation of increased antioxidant enzymes (SOD and CAT) activities in the serum and heart of the treated rats. MOE normalized the elevated TNF-α and IL-1β in serum and heart tissues. Furthermore, the IgG titre value was significantly (p < 0.5) higher in the envenomed untreated group compared to the MOE-treated groups. Hemorrhagic, hemolytic and coagulant activities of the venom were strongly inhibited by the MOE dose, dependently. Lesions noticed on tissues of vital organs of untreated rats were abolished by MOE. Our findings substantiate the effectiveness of MOE as a potential remedy against EOV toxicities.
Keywords: Echis ocellatus; Moringa oleifera; antivenom; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Moringa oleifera leaf fractions attenuated Naje haje venom-induced cellular dysfunctions via modulation of Nrf2 and inflammatory signalling pathways in rats.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021 Jan 20;25:100890. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2020.100890. eCollection 2021 Mar. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021. PMID: 33521334 Free PMC article.
-
Kaempferol from Moringa oleifera demonstrated potent antivenom activities via inhibition of metalloproteinase and attenuation of Bitis arietans venom-induced toxicities.Toxicon. 2023 Sep;233:107242. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2023.107242. Epub 2023 Aug 8. Toxicon. 2023. PMID: 37558138
-
Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract Attenuates Pb Acetate-induced Testicular Damage in Rats.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2021;24(10):1593-1602. doi: 10.2174/1386207323666200923142831. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2021. PMID: 32964820
-
Antivenom therapy of carpet viper (Echis ocellatus) envenoming: effectiveness and strategies for delivery in West Africa.Toxicon. 2013 Jul;69:82-9. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2013.01.002. Epub 2013 Jan 20. Toxicon. 2013. PMID: 23339853 Review.
-
Prospects for Protective Potential of Moringa oleifera against Kidney Diseases.Plants (Basel). 2021 Dec 20;10(12):2818. doi: 10.3390/plants10122818. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34961289 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of oral toxicity of Moringa oleifera Lam aqueous extract and its effect on gout induced in a murine model.Vet World. 2024 Jul;17(7):1449-1458. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2024.1449-1458. Epub 2024 Jul 7. Vet World. 2024. PMID: 39185060 Free PMC article.
-
Varespladib attenuates Naja atra-induced acute liver injury via reversing Nrf2 signaling-mediated ferroptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction.Redox Rep. 2025 Dec;30(1):2507557. doi: 10.1080/13510002.2025.2507557. Epub 2025 May 21. Redox Rep. 2025. PMID: 40399141 Free PMC article.
-
Echis ocellatus Venom-Induced Reproductive Pathologies in Rat Model; Roles of Oxidative Stress and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines.Toxins (Basel). 2022 May 29;14(6):378. doi: 10.3390/toxins14060378. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35737039 Free PMC article.
-
Echis ocellatus venom-induced sperm functional deficits, pro-apoptotic and inflammatory activities in male reproductive organs in rats: antagonistic role of kaempferol.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2024 Aug 9;25(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s40360-024-00776-0. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39123263 Free PMC article.
-
Using a Machine Learning Approach to Predict Snakebite Envenoming Outcomes Among Patients Attending the Snakebite Treatment and Research Hospital in Kaltungo, Northeastern Nigeria.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2025 Apr 11;10(4):103. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed10040103. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40278776 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Onyeama H.P., Ebong P.E., Eteng M.U., Igile G.O., Ofemile P.Y., Ibekwe H.A. Histological Reponses of the heart, liver and kidney to Calliandra portoricensis extracts in Wistar rats challenged with venom of Echis ocellatus. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2012;2:164–171.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
