Molecular Functions of Hydrogen Sulfide in Cancer
- PMID: 35366284
- PMCID: PMC8830448
- DOI: 10.3390/pathophysiology28030028
Molecular Functions of Hydrogen Sulfide in Cancer
Abstract
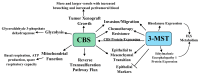
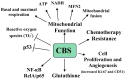
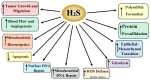
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is a gasotransmitter that exerts a multitude of functions in both physiologic and pathophysiologic processes. H2S-synthesizing enzymes are increased in a variety of human malignancies, including colon, prostate, breast, renal, urothelial, ovarian, oral squamous cell, and thyroid cancers. In cancer, H2S promotes tumor growth, cellular and mitochondrial bioenergetics, migration, invasion, angiogenesis, tumor blood flow, metastasis, epithelia-mesenchymal transition, DNA repair, protein sulfhydration, and chemotherapy resistance Additionally, in some malignancies, increased H2S-synthesizing enzyme expression correlates with a worse prognosis and a higher tumor stage. Here we review the role of H2S in cancer, with an emphasis on the molecular mechanisms by which H2S promotes cancer development, progression, dedifferentiation, and metastasis.
Keywords: 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase; H2S; cancer; cystathionine β-synthase; cystathionine γ-lyase; hydrogen sulfide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Nicholson R.A., Roth S.H., Zhang A., Brookes J., Skrajny B., Bennington R. Inhibition of respiratory and bioenergetic mechanisms by hydrogen sulfide in mammalian brain. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A. 1998;54:491–507. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
