The novel protein ScrA acts through the SaeRS two-component system to regulate virulence gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 35366366
- PMCID: PMC9324805
- DOI: 10.1111/mmi.14901
The novel protein ScrA acts through the SaeRS two-component system to regulate virulence gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
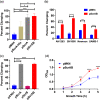
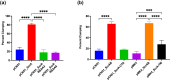
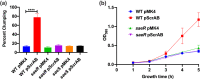
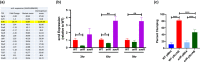
Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram-positive commensal that can also cause a variety of infections in humans. S. aureus virulence factor gene expression is under tight control by a complex regulatory network, which includes, sigma factors, sRNAs, and two-component systems (TCS). Previous work in our laboratory demonstrated that overexpression of the sRNA tsr37 leads to an increase in bacterial aggregation. Here, we demonstrate that the clumping phenotype is dependent on a previously unannotated 88 amino acid protein encoded within the tsr37 sRNA transcript (which we named ScrA for S. aureus clumping regulator A). To investigate the mechanism of action of ScrA we performed proteomics and transcriptomics in a ScrA overexpressing strain and show that a number of surface adhesins are upregulated, while secreted proteases are downregulated. Results also showed upregulation of the SaeRS TCS, suggesting that ScrA is influencing SaeRS activity. Overexpression of ScrA in a saeR mutant abrogates the clumping phenotype confirming that ScrA functions via the Sae system. Finally, we identified the ArlRS TCS as a positive regulator of scrA expression. Collectively, our results show that ScrA is an activator of the SaeRS system and suggests that ScrA may act as an intermediary between the ArlRS and SaeRS systems.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; SaeRS; small proteins; virulence.
© 2022 The Authors. Molecular Microbiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures




References
-
- Bronesky, D. , Wu, Z. , Marzi, S. , Walter, P. , Geissmann, T. , Moreau, K. et al. (2016) Staphylococcus aureus RNAIII and its regulon link quorum sensing, stress responses, metabolic adaptation, and regulation of virulence gene expression. Annual Review of Microbiology, 70, 299–316. 10.1146/annurev-micro-102215-095708 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Carroll, R.K. , Robison, T.M. , Rivera, F.E. , Davenport, J.E. , Jonsson, I.M. , Florczyk, D. et al. (2012) Identification of an intracellular M17 family leucine aminopeptidase that is required for virulence in Staphylococcus aureus . Microbes and Infection, 14, 989–999. 10.1016/j.micinf.2012.04.013 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

