Effects of duck circovirus on immune function and secondary infection of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli
- PMID: 35366422
- PMCID: PMC8971308
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.101799
Effects of duck circovirus on immune function and secondary infection of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli
Abstract
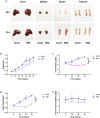
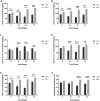
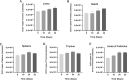
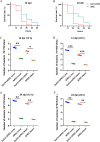
Duck circovirus (DuCV) infection occurs frequently in ducks in China and is generally believed to lead to immunosuppression and secondary infection, though there has been a lack of detailed research and direct evidence. In this study, one-day-old Cherry Valley ducklings were artificially infected with DuCV alone and co-infected with DuCV and Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC). The immune indexes at 32 d old were systematically monitored, including immune organ weight, lymphocyte transformation rate, IL-10, IL-12, soluble CD4 (sCD4), soluble CD8 (sCD8), IFN-γ, viral loads in each organ, APEC colonization, and so on. The results showed the development of immune organs in ducklings was affected, resulting in a decrease in the lymphocyte transformation rate (LTR), IL-12, sCD4, sCD8, IFN-γ and an increase in IL-10 content at 8 to 32 d postinfection (dpi). In the detection of virus loads in some organs, it was found that 8 dpi, DuCV existed stably in various organs, suggesting the importance of preventing and controlling the virus in the early stage of culture. The results of exploring the DuCV infection that shows some influence on secondary infection by APEC. The results showed that DuCV infection could significantly enhance the pathogenicity of APEC and the colonization ability of APEC in vivo. DuCV can induce more serious APEC infection in 24 dpi than in 14 dpi. Based on the above results, it can be concluded that DuCV infection will affect the immune system, cause immunosuppression, and lead to more serious secondary infection.
Keywords: Avian pathogenic Escherichia Coli; duck circovirus; immunosuppression; secondary infection.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Duck circovirus regulates the expression of duck CLDN2 protein by activating the MAPK-ERK pathway to affect its adhesion and infection.J Virol. 2024 Oct 22;98(10):e0049724. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00497-24. Epub 2024 Sep 30. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39345142 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the infection characteristics and pathogenesis of duck circovirus 1 in Cherry Valley meat ducks.Poult Sci. 2025 Feb;104(2):104805. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.104805. Epub 2025 Jan 11. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 39813864 Free PMC article.
-
An investigation of duck circovirus and co-infection in Cherry Valley ducks in Shandong Province, China.Vet Microbiol. 2009 Jan 13;133(3):252-6. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2008.07.005. Epub 2008 Jul 25. Vet Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 18760549
-
From obscurity to urgency: a comprehensive analysis of the rising threat of duck circovirus.Vet Res. 2024 Jan 26;55(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s13567-024-01265-2. Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 38279181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC)].Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2003 Sep-Oct;116(9-10):381-95. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2003. PMID: 14526468 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Canine Circovirus Suppresses the Type I Interferon Response and Protein Expression but Promotes CPV-2 Replication.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 7;23(12):6382. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126382. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35742826 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of circovirus immunosuppression and pathogenesis with a focus on porcine circovirus 2: a review.Vet Q. 2023 Dec;43(1):1-18. doi: 10.1080/01652176.2023.2234430. Vet Q. 2023. PMID: 37431709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR/Cas12a and recombinase polymerase amplification-based rapid on-site nucleic acid detection of duck circovirus.Virol J. 2024 Dec 19;21(1):322. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02577-7. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 39702333 Free PMC article.
-
Duck circovirus regulates the expression of duck CLDN2 protein by activating the MAPK-ERK pathway to affect its adhesion and infection.J Virol. 2024 Oct 22;98(10):e0049724. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00497-24. Epub 2024 Sep 30. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39345142 Free PMC article.
-
Feeding live yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) improved performance of mid-lactation dairy cows by altering ruminal bacterial communities and functions of serum antioxidation and immune responses.BMC Vet Res. 2024 Jun 7;20(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04073-0. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 38849835 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bertram E.M., Jilbert A.R., Kotlarski I. Optimization of an in vitro assay which measures the proliferation of duck T lymphocytes from peripheral blood in response to stimulation with PHA and ConA. Dev. Compar. Immunol. 1997;21:299–310. - PubMed
-
- De Rie M.A., Zonneveld I.M., Witkamp L., Van Lier R.A., Out T.A., Bos J.D. Soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R) is a marker of disease activity in psoriasis: a comparison of sIL-2R, sCD27, sCD4, sCD8 and sICAM-1. Acta Derm Venereol. 1996;76:357–360. - PubMed
-
- Docke W.-D., Asadullah K., Belbe G., Ebeling M., Hoflich C., Friedrich M., Sterry W., Volk H.-D. Comprehensive biomarker monitoring in cytokine therapy: Heterogeneous, time-dependent, and persisting immune effects of interleukin-10 application in psoriasis. J. Leukocyte Biol. 2009;85:582–593. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

