PyToxo: a Python tool for calculating penetrance tables of high-order epistasis models
- PMID: 35366804
- PMCID: PMC8977015
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-022-04645-7
PyToxo: a Python tool for calculating penetrance tables of high-order epistasis models
Abstract
Background: Epistasis is the interaction between different genes when expressing a certain phenotype. If epistasis involves more than two loci it is called high-order epistasis. High-order epistasis is an area under active research because it could be the cause of many complex traits. The most common way to specify an epistasis interaction is through a penetrance table.
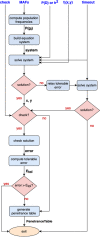
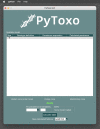
Results: This paper presents PyToxo, a Python tool for generating penetrance tables from any-order epistasis models. Unlike other tools available in the bibliography, PyToxo is able to work with high-order models and realistic penetrance and heritability values, achieving high-precision results in a short time. In addition, PyToxo is distributed as open-source software and includes several interfaces to ease its use.
Conclusions: PyToxo provides the scientific community with a useful tool to evaluate algorithms and methods that can detect high-order epistasis to continue advancing in the discovery of the causes behind complex diseases.
Keywords: Epistasis model; Gene interaction; Heritability; Penetrance; Prevalence; Python; Simulation; SymPy.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Shang J, Zhang J, Lei X, Zhao W, Dong Y. EpiSIM: simulation of multiple epistasis, linkage disequilibrium patterns and haplotype blocks for genome-wide interaction analysis. Genes Genomics. 2013;35(3):305–16. doi: 10.1007/s13258-013-0081-9. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources