Clinical value of serum cholinesterase levels in Nephrotic syndrome: an observational study
- PMID: 35366840
- PMCID: PMC8976987
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-022-02764-0
Clinical value of serum cholinesterase levels in Nephrotic syndrome: an observational study
Abstract
Background: Nephrotic syndrome (NS) results in massive proteinuria and hypoalbuminemia, which are responsible for a compensatory increase in protein synthesis in the liver. Serum cholinesterase (ChE) also increases in NS. However, its clinical value is not fully elucidated.
Methods: In this study, 184 patients with NS who underwent kidney biopsy were included. The patients were divided into two groups according to serum ChE levels, as follows: hypercholinesterasemia (HC) and non-hypercholinesterasemia (NHC) groups. The clinical factors were compared between the two groups.
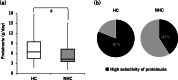
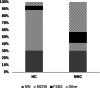
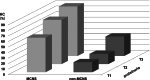
Results: The HC group had significantly more severe proteinuria and higher prevalence of high selective proteinuria than the NHC group. Furthermore, the prevalence of minimal change nephrotic syndrome (MCNS) was significantly higher in the HC group than that in the NHC group. Multivariate analysis revealed that the severity of proteinuria and MCNS were significantly associated with HC.
Conclusion: In this study, HC in NS was associated with the severity of proteinuria and MCNS, and could help clinicians predict the histological diagnosis of NS.
Keywords: Cholinesterase; Minimal change nephrotic syndrome; Nephrotic syndrome.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kodner C. Diagnosis and management of nephrotic syndrome in adults. Am Fam Physician. 2016;93:479–485. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

