Bacteria-driven hypoxia targeting delivery of chemotherapeutic drug proving outcome of breast cancer
- PMID: 35366890
- PMCID: PMC8976953
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-022-01373-1
Bacteria-driven hypoxia targeting delivery of chemotherapeutic drug proving outcome of breast cancer
Abstract
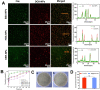
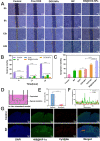
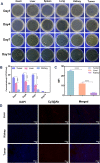
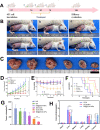
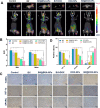
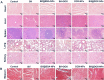
Local hypoxia is a common feature of many solid tumors and may lead to unsatisfactory chemotherapy outcomes. Anaerobic bacteria that have an affinity to hypoxic areas can be used to achieve targeted drug delivery in tumor tissues. In this study, we developed a biocompatible bacteria/nanoparticles biohybrid (Bif@DOX-NPs) platform that employs the anaerobic Bifidobacterium infantis (Bif) to deliver adriamycin-loaded bovine serum albumin nanoparticles (DOX-NPs) into breast tumors. The Bif@DOX-NPs retained the targeting ability of B. infantis to hypoxic regions, as well as the cytotoxicity of DOX. The biohybrids were able to actively colonize the hypoxic tumors and significantly increased drug accumulation at the tumor site. The DOX concentration in the tumor masses colonized by Bif@DOX-NPs was 4 times higher than that in the free DOX-treated tumors, which significantly prolonged the median survival of the tumor-bearing mice to 69 days and reduced the toxic side-effects of DOX. Thus, anaerobic bacteria-based biohybrids are a highly promising tool for the targeted treatment of solid tumors with inaccessible hypoxic regions.
Keywords: Albumin nanoparticles; Bifidobacterium infantis; Biohybrid; Breast cancer; Tumor hypoxia.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Brown J, Wilson W. Exploiting tumour hypoxia in cancer treatment. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:437–447. - PubMed
-
- Han K, Wang S, Lei Q, Zhu J, Zhang X. Ratiometric biosensor for aggregation-induced emission-guided precise photodynamic therapy. ACS Nano. 2015;9:10268–10277. - PubMed
-
- Liu S, Minton N, Giaccia A, Brown J. Anticancer efficacy of systemically delivered anaerobic bacteria as gene therapy vectors targeting tumor hypoxia/necrosis. Gene Ther. 2002;9:291–296. - PubMed
-
- Yu Y, Shabahang S, Timiryasova T, Zhang Q, Beltz R, Gentschev I, Goebel W, Szalay A. Visualization of tumors and metastases in live animals with bacteria and vaccinia virus encoding light-emitting proteins. Nat Biotechnol. 2004;22:313–320. - PubMed
-
- Broadway K, Suh S, Behkam B, Scharf B. Optimizing the restored chemotactic behavior of anticancer agent Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium VNP20009. J Biotechnol. 2017;251:76–83. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

