New diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for myocardial infarction via nanomaterials
- PMID: 35367772
- PMCID: PMC8983382
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103968
New diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for myocardial infarction via nanomaterials
Abstract
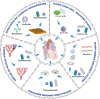
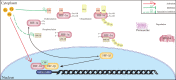
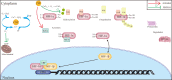
Myocardial infarction is lethal to patients because of insufficient blood perfusion to vital organs. Several attempts have been made to improve its prognosis, among which nanomaterial research offers an opportunity to address this problem at the molecular level and has the potential to improve disease prevention, diagnosis, and treatment significantly. Up to now, nanomaterial-based technology has played a crucial role in broad novel diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for cardiac repair. This review summarizes various nanomaterial applications in myocardial infarction from multiple aspects, including high precision detection, pro-angiogenesis, regulating immune homeostasis, and miRNA and stem cell delivery vehicles. We also propose promising research hotspots that have not been reported much yet, such as conjugating pro-angiogenetic elements with nanoparticles to construct drug carriers, developing nanodrugs targeting other immune cells except for macrophages in the infarcted myocardium or the remote region. Though most of those strategies are preclinical and lack clinical trials, there is tremendous potential for their further applications in the future.
Keywords: Cardiac biomarker; Ischaemic heart disease; Myocardial infarction; Nano-delivery system; Nanomaterials; New diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Dariush Mozaffarian E.J.B., Go A.S., Arnett D.K., et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2015 update a report from the American heart association. Circulation. 2015;131(4):e29–e322. - PubMed
-
- Organization W.H. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). June 11 2021. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases.... Accessed 24 July 2021.
-
- Zasada W., Bobrowska B., Plens K., et al. Acute myocardial infarction in young patients. Kardiol Pol. 2021 - PubMed
-
- Virani S.S., Alonso A., Benjamin E.J., et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2020 update: a report from the American heart association. Circulation. 2020;141(9):e139–e596. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

