Exploring Network Properties Across Preclinical Stages of Alzheimer's Disease Using a Visual Short-Term Memory and Attention Task with High-Density Electroencephalography: A Brain-Connectome Neurophysiological Study
- PMID: 35367964
- PMCID: PMC9661343
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-215421
Exploring Network Properties Across Preclinical Stages of Alzheimer's Disease Using a Visual Short-Term Memory and Attention Task with High-Density Electroencephalography: A Brain-Connectome Neurophysiological Study
Abstract
Background: Visual short-term memory (VSTMT) and visual attention (VAT) exhibit decline in the Alzheimer's disease (AD) continuum; however, network disruption in preclinical stages is scarcely explored.
Objective: To advance our knowledge about brain networks in AD and discover connectivity alterations during VSTMT and VAT.
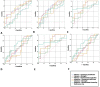
Methods: Twelve participants with AD, 23 with mild cognitive impairment (MCI), 17 with subjective cognitive decline (SCD), and 21 healthy controls (HC) were examined using a neuropsychological battery at baseline and follow-up (three years). At baseline, the subjects were examined using high density electroencephalography while performing a VSTMT and VAT. For exploring network organization, we constructed weighted undirected networks and examined clustering coefficient, strength, and betweenness centrality from occipito-parietal regions.
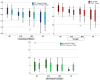
Results: One-way ANOVA and pair-wise t-test comparisons showed statistically significant differences in HC compared to SCD (t (36) = 2.43, p = 0.026), MCI (t (42) = 2.34, p = 0.024), and AD group (t (31) = 3.58, p = 0.001) in Clustering Coefficient. Also with regards to Strength, higher values for HC compared to SCD (t (36) = 2.45, p = 0.019), MCI (t (42) = 2.41, p = 0.020), and AD group (t (31) = 3.58, p = 0.001) were found. Follow-up neuropsychological assessment revealed converge of 65% of the SCD group to MCI. Moreover, SCD who were converted to MCI showed significant lower values in all network metrics compared to the SCD that remained stable.
Conclusion: The present findings reveal that SCD exhibits network disorganization during visual encoding and retrieval with intermediate values between MCI and HC.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; brain networks; electroencephalography; mild cognitive impairment; subjective cognitive decline; visual attention; visual short-term memory.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ disclosures available online (
Figures


References
-
- (2021) 2021 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement 17, 327–406. - PubMed
-
- Gauthier S, Reisberg B, Zaudig M, Petersen RC, Ritchie K, Broich K, Belleville S, Brodaty H, Bennett D, Chertkow H, Cummings JL, de Leon M, Feldman H, Ganguli M, Hampel H, Scheltens P, Tierney MC, Whitehouse P, Winblad B (2006) Mild cognitive impairment. Lancet 367, 1262–1270. - PubMed
-
- Mohs RC, Knopman D, Petersen RC, Ferris SH, Ernesto C, Grundman M, Sano M, Bieliauskas L, Geldmacher D, Clark C, Thal LJ (1997) Development of cognitive instruments for use in clinical trials of antidementia drugs: Additions to the Alzheimer’s disease assessment scale that broaden its scope. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 11, S13–21. - PubMed
-
- Slot RER, Sikkes SAM, Berkhof J, Brodaty H, Buckley R, Cavedo E, Dardiotis E, Guillo-Benarous F, Hampel H, Kochan NA, Lista S, Luck T, Maruff P, Molinuevo JL, Kornhuber J, Reisberg B, Riedel-Heller SG, Risacher SL, Roehr S, Sachdev PS, Scarmeas N, Scheltens P, Shulman MB, Saykin AJ, Verfaillie SCJ, Visser PJ, Vos SJB, Wagner M, Wolfsgruber S, Jessen F, Boada M, de Deyn PP, Jones R, Frisoni G, Spiru L, Nobili F, Freund-Levi Y, Soininen H, Verhey F, Wallin ÅK, Touchon J, Rikkert MO, Rigaud AS, Bullock R, Tsolaki M, Vellas B, Wilcock G, Froelich L, Bakardjian H, Benali H, Bertin H, Bonheur J, Boukadida L, Boukerrou N, Chiesa P, Colliot O, Dubois B, Dubois M, Epelbaum S, Gagliardi G, Genthon R, Habert MO, Houot M, Kas A, Lamari F, Levy M, Metzinger C, Mochel F, Nyasse F, Poisson C, Potier MC, Revillon M, Santos A, Andrade KS, Sole M, Surtee M, Thiebaud de Schotten M, Vergallo A, Younsi N, van der Flier WM (2019) Subjective cognitive decline and rates of incident Alzheimer’s disease and non-Alzheimer’s disease dementia. Alzheimers Dement 15, 465–476. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Verfaillie SCJ, Binette AP, Vachon-Presseau É, Tabrizi S, Savard M, Bellec P, Ossenkoppele R, Scheltens P, van der Flier WM, Breitner JCS, Villeneuve S (2017) Subjective cognitive decline is associated with altered posterior cingulate connectivity in elderly with a familial history of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 13, P33–P34.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

