Lipidomic Profiling of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Extracellular Vesicles Indicates Their Involvement in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury
- PMID: 35367992
- PMCID: PMC9485986
- DOI: 10.1159/000522338
Lipidomic Profiling of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Extracellular Vesicles Indicates Their Involvement in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury
Abstract
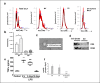
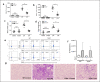
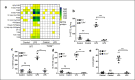
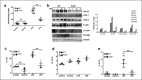
Emerging data support the pivotal role of extracellular vesicles (EVs) in normal cellular physiology and disease conditions. However, despite their abundance, there is much less information about the lipid mediators carried in EVs, especially in the context of acute lung injury (ALI). Our data demonstrate that C57BL/6 mice subjected to intranasal Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced ALI release, a higher number of EVs into the alveolar space, compared to saline-treated controls. EVs released during ALI originated from alveolar epithelial cells, macrophages, and neutrophils and carry a diverse array of lipid mediators derived from ω-3 and ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA). The eicosanoids in EVs correlated with cellular levels of arachidonic acid, expression of cytosolic phospholipase A2, cyclooxygenase (COX), lipoxygenase (LOX), and cytochrome epoxygenase p450 proteins in pulmonary macrophages. Furthermore, EVs from LPS-toll-like receptor 4 knockout (TLR4-/-) mice contained significantly lower amounts of COX and LOX catalyzed eicosanoids and ω-3 PUFA metabolites. More importantly, EVs from LPS-treated wild-type mice increased TNF-α release by macrophages and reduced alveolar epithelial monolayer barrier integrity compared to EVs from LPS-treated TLR4-/- mice. In summary, our study demonstrates for the first time that the EV carried PUFA metabolite profile in part depends on the inflammatory status of the lung macrophages and modulates pulmonary macrophage and alveolar epithelial cell function during LPS-induced ALI.
Keywords: Acute lung injury; Extracellular vesicles; Inflammation; Macrophage; Polyunsaturated fatty acids.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures


References
-
- Herrero R, Rojas Y, Esteban A. Novel pharmacologic approaches for the treatment of ARDS. In: Vincent JL, editor. Annual update in intensive care and emergency medicine 2014. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2014. pp. 231–43.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

