Beyond Genes: Inclusion of Alternative Splicing and Alternative Polyadenylation to Assess the Genetic Architecture of Predisposition to Voluntary Alcohol Consumption in Brain of the HXB/BXH Recombinant Inbred Rat Panel
- PMID: 35368676
- PMCID: PMC8965255
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.821026
Beyond Genes: Inclusion of Alternative Splicing and Alternative Polyadenylation to Assess the Genetic Architecture of Predisposition to Voluntary Alcohol Consumption in Brain of the HXB/BXH Recombinant Inbred Rat Panel
Abstract
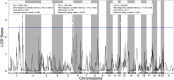
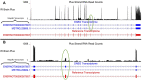
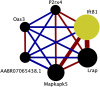
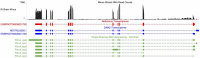
Post transcriptional modifications of RNA are powerful mechanisms by which eukaryotes expand their genetic diversity. For instance, researchers estimate that most transcripts in humans undergo alternative splicing and alternative polyadenylation. These splicing events produce distinct RNA molecules, which in turn yield distinct protein isoforms and/or influence RNA stability, translation, nuclear export, and RNA/protein cellular localization. Due to their pervasiveness and impact, we hypothesized that alternative splicing and alternative polyadenylation in brain can contribute to a predisposition for voluntary alcohol consumption. Using the HXB/BXH recombinant inbred rat panel (a subset of the Hybrid Rat Diversity Panel), we generated over one terabyte of brain RNA sequencing data (total RNA) and identified novel splice variants (via StringTie) and alternative polyadenylation sites (via aptardi) to determine the transcriptional landscape in the brains of these animals. After establishing an analysis pipeline to ascertain high quality transcripts, we quantitated transcripts and integrated genotype data to identify candidate transcript coexpression networks and individual candidate transcripts associated with predisposition to voluntary alcohol consumption in the two-bottle choice paradigm. For genes that were previously associated with this trait (e.g., Lrap, Ift81, and P2rx4) (Saba et al., Febs. J., 282, 3556-3578, Saba et al., Genes. Brain. Behav., 20, e12698), we were able to distinguish between transcript variants to provide further information about the specific isoforms related to the trait. We also identified additional candidate transcripts associated with the trait of voluntary alcohol consumption (i.e., isoforms of Mapkapk5, Aldh1a7, and Map3k7). Consistent with our previous work, our results indicate that transcripts and networks related to inflammation and the immune system in brain can be linked to voluntary alcohol consumption. Overall, we have established a pipeline for including the quantitation of alternative splicing and alternative polyadenylation variants in the transcriptome in the analysis of the relationship between the transcriptome and complex traits.
Keywords: HXB/BXH recombinant inbred panel; RNA-seq—RNA sequencing; alternative polyadenylation; alternative splicing; isoform; transcriptome; voluntary alcohol consumption; weighted gene co expression network analysis.
Copyright © 2022 Lusk, Hoffman, Mahaffey, Rosean, Smith, Silhavy, Pravenec, Tabakoff and Saba.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

