Lung Disease Classification in CXR Images Using Hybrid Inception-ResNet-v2 Model and Edge Computing
- PMID: 35368941
- PMCID: PMC8968389
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/9036457
Lung Disease Classification in CXR Images Using Hybrid Inception-ResNet-v2 Model and Edge Computing
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Lung Disease Classification in CXR Images Using Hybrid Inception-ResNet-v2 Model and Edge Computing.J Healthc Eng. 2023 May 24;2023:9826867. doi: 10.1155/2023/9826867. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37266284 Free PMC article.
Abstract
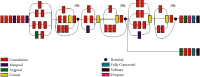
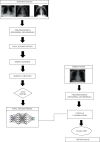
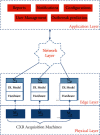
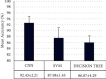
Chest X-ray (CXR) imaging is one of the most widely used and economical tests to diagnose a wide range of diseases. However, even for expert radiologists, it is a challenge to accurately diagnose diseases from CXR samples. Furthermore, there remains an acute shortage of trained radiologists worldwide. In the present study, a range of machine learning (ML), deep learning (DL), and transfer learning (TL) approaches have been evaluated to classify diseases in an openly available CXR image dataset. A combination of the synthetic minority over-sampling technique (SMOTE) and weighted class balancing is used to alleviate the effects of class imbalance. A hybrid Inception-ResNet-v2 transfer learning model coupled with data augmentation and image enhancement gives the best accuracy. The model is deployed in an edge environment using Amazon IoT Core to automate the task of disease detection in CXR images with three categories, namely pneumonia, COVID-19, and normal. Comparative analysis has been given in various metrics such as precision, recall, accuracy, AUC-ROC score, etc. The proposed technique gives an average accuracy of 98.66%. The accuracies of other TL models, namely SqueezeNet, VGG19, ResNet50, and MobileNetV2 are 97.33%, 91.66%, 90.33%, and 76.00%, respectively. Further, a DL model, trained from scratch, gives an accuracy of 92.43%. Two feature-based ML classification techniques, namely support vector machine with local binary pattern (SVM + LBP) and decision tree with histogram of oriented gradients (DT + HOG) yield an accuracy of 87.98% and 86.87%, respectively.
Copyright © 2022 Chandra Mani Sharma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Sahlol A. T., Abd Elaziz M., Tariq Jamal A., Damaševičius R., Farouk Hassan O. A novel method for detection of tuberculosis in chest radiographs using artificial ecosystem-based optimisation of deep neural network features. Symmetry . 2020;12(7):p. 1146. doi: 10.3390/sym12071146. - DOI
-
- Poap D., Wozniak M., Damaševičius R., Wei W. Chest radiographs segmentation by the use of nature-inspired algorithm for lung disease detection. Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI); November 2018; Bangalore, India. IEEE; pp. 2298–2303. - DOI
-
- Rahman. CXR data set repository. 2020. https://bit.ly/3p6KtQD Kaggle.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

