Automated System for Identifying COVID-19 Infections in Computed Tomography Images Using Deep Learning Models
- PMID: 35368962
- PMCID: PMC8968354
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5329014
Automated System for Identifying COVID-19 Infections in Computed Tomography Images Using Deep Learning Models
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Automated System for Identifying COVID-19 Infections in Computed Tomography Images Using Deep Learning Models.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Oct 11;2023:9812058. doi: 10.1155/2023/9812058. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37860421 Free PMC article.
Abstract
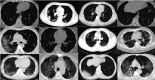
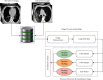
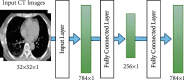
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a novel disease that affects healthcare on a global scale and cannot be ignored because of its high fatality rate. Computed tomography (CT) images are presently being employed to assist doctors in detecting COVID-19 in its early stages. In several scenarios, a combination of epidemiological criteria (contact during the incubation period), the existence of clinical symptoms, laboratory tests (nucleic acid amplification tests), and clinical imaging-based tests are used to diagnose COVID-19. This method can miss patients and cause more complications. Deep learning is one of the techniques that has been proven to be prominent and reliable in several diagnostic domains involving medical imaging. This study utilizes a convolutional neural network (CNN), stacked autoencoder, and deep neural network to develop a COVID-19 diagnostic system. In this system, classification undergoes some modification before applying the three CT image techniques to determine normal and COVID-19 cases. A large-scale and challenging CT image dataset was used in the training process of the employed deep learning model and reporting their final performance. Experimental outcomes show that the highest accuracy rate was achieved using the CNN model with an accuracy of 88.30%, a sensitivity of 87.65%, and a specificity of 87.97%. Furthermore, the proposed system has outperformed the current existing state-of-the-art models in detecting the COVID-19 virus using CT images.
Copyright © 2022 Karrar Hameed Abdulkareem et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Toğaçar M., Muzoğlu N., Ergen B., Yarman B. S. B., Halefoğlu A. M. Detection of COVID-19 findings by the local interpretable model-agnostic explanations method of types-based activations extracted from CNNs. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control . 2022;71 doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103128.103128 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

