Potential Role of Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) in the Prevention of Neurodegenerative Diseases
- PMID: 35369082
- PMCID: PMC8971783
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.809621
Potential Role of Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) in the Prevention of Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
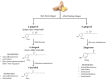
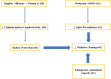
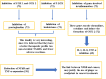
Ginger is composed of multiple bioactive compounds, including 6-gingerol, 6-shogaol, 10-gingerol, gingerdiones, gingerdiols, paradols, 6-dehydrogingerols, 5-acetoxy-6-gingerol, 3,5-diacetoxy-6-gingerdiol, and 12-gingerol, that contribute to its recognized biological activities. Among them, the major active compounds are 6-shogaol and 6-gingerol. Scientific evidence supports the beneficial properties of ginger, including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacities and in contrast, a specific and less studied bioactivity is the possible neuroprotective effect. The increase in life expectancy has raised the incidence of neurodegenerative diseases (NDs), which present common neuropathological features as increased oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and protein misfolding. The structure-activity relationships of ginger phytochemicals show that ginger can be a candidate to treat NDs by targeting different ligand sites. Its bioactive compounds may improve neurological symptoms and pathological conditions by modulating cell death or cell survival signaling molecules. The cognitive enhancing effects of ginger might be partly explained via alteration of both the monoamine and the cholinergic systems in various brain areas. Moreover, ginger decreases the production of inflammatory related factors. The aim of the present review is to summarize the effects of ginger in the prevention of major neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and multiple sclerosis.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Parkinson's disease; antioxidants; ginger; gingerol; multiple sclerosis; neurodegenerative diseases.
Copyright © 2022 Arcusa, Villaño, Marhuenda, Cano, Cerdà and Zafrilla.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mann A. Biopotency role of culinary spices and herbs and their chemical constituents in health and commonly used spices in Nigerian dishes and snacks. African J Food Sci. (2011) 5:111–24. 10.5897/AJFS.9000032 - DOI
-
- Banerjee S, Mullick HI, Banerjee J. Ghosh A. Zingiber officinale:‘a natural gold'. Int J Pharm Bio-Sci. (2011) 2:283–94.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

