Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Predicts Short-Term Prognosis in Patients With Acute Heart Failure: A Prospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 35369322
- PMCID: PMC8965840
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.834967
Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Predicts Short-Term Prognosis in Patients With Acute Heart Failure: A Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: Recent studies of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), first recognized as a regulator of glucose and lipid metabolism, have found that the level of in serum FGF21 is associated with the prognosis of many cardiovascular diseases, but its relationship to acute heart failure (AHF) patients remains unknown. Our study aimed to investigate whether circulating FGF21 could predict the short-term prognosis of AHF patients.
Methods: Four hundred and two AHF patients and 19 healthy controls were recruited into the prospective cohort study, and blood samples of participants were collected, in tubes without anticoagulant, within the first 24 h after hospital admission. Serum FGF21 levels were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). All patients were followed-up at least 6 months after discharge. The primary endpoint was all-cause death, and secondary endpoint was a composite endpoint of death and heart failure readmission. Mortality and composite end point events were analyzed using Kaplan-Meier curves. ROC curves compared the difference between the FGF21 and NT-proBNP in predicting 3- and 6-months mortality. Time-to-event data were evaluated using Kaplan-Meier estimation and Cox proportional hazards models.
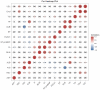
Results: In the present study, the serum FGF21 concentrations were significantly higher in the 402 AHF patients enrolled, compared with the 19 healthy controls (p < 0.001). The average age was 70 (±12) years, and 58% were males. Participants were divided into two groups according to the median FGF21 level (262 pg/ml): a high FGF21 group (n = 201, FGF21 ≥ 262 pg/ml) and low FGF21 group (n = 201, FGF21 <262 pg/ml). FGF21 was positively correlated with NT-proBNP, BUN, AST, creatinine and cholesterol, and negatively correlated with ALB and HDL. After a median follow-up of 193 days, the high FGF21 group had higher mortality and composite endpoint events compared with the low FGF21 group (HR: 3.91, 95% CI 2.21-6.92, p <0.001), even after adjusting for NT-proBNP (HR: 3.17, 95% CI 1.72-5.81, p < 0.001). ROC analysis shows that FGF21 was better than NT-proBNP in predicting death at both 3 (AUC, 0.77 vs. 0.63, p < 0.001) and 6 months (AUC, 0.78 vs. 0.66).
Conclusion: High baseline FGF21 levels are associated with adverse clinical outcomes in AHF patients. Serum FGF21 might be a potential predictive biomarker of AHF patients.
Keywords: FGF21; acute heart failure; biomarker; death; prognosis.
Copyright © 2022 Wu, Wu, Yan, Gao, Zhu, Yue, Li and Tan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


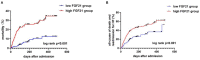

References
-
- van den Berge JC, Constantinescu AA, van Domburg RT, Brankovic M, Deckers JW, Akkerhuis, et al. Renal function and anemia in relation to short- and long-term prognosis of patients with acute heart failure in the period 1985-2008: a clinical cohort study. PLoS ONE. (2018) 13:e0201714. 10.1371/journal.pone.0201714 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

