Glaucocalyxin A alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and apoptosis in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells and permeability injury by inhibiting STAT3 signaling
- PMID: 35369532
- PMCID: PMC8943557
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2022.11242
Glaucocalyxin A alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and apoptosis in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells and permeability injury by inhibiting STAT3 signaling
Abstract
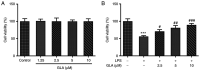
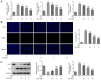
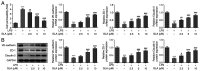
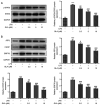
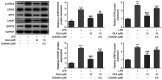
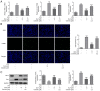
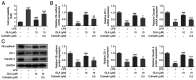
Glaucocalyxin A (GLA), an ent-kauranoid diterpene derived from Rabdosia japonica var. glaucocalyx, possesses antibacterial, anti-oxidative and anti-neuroinflammatory properties. The present study aimed to investigate the potential mechanisms underlying GLA in the pathogenesis of pneumonia. Human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (hPMVECs) treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) were treated with GLA, followed by the detection of cell viability, inflammation, apoptosis and cell permeability. Furthermore, the protein expression levels of apoptosis- and permeability-associated proteins were determined using western blot analysis. Following treatment with a signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) activator, the protein expression levels of STAT3 and endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated proteins were determined, to confirm whether STAT3 signaling was mediated by GLA. Lastly, the mRNA expression level of inflammatory cytokines, apoptosis and permeability injury were also determined following treatment with a STAT3 activator. The results revealed that GLA ameliorated inflammation, apoptosis and permeability injury in LPS-induced hPMVECs. Following treatment with a STAT3 activator, the therapeutic effects of GLA on LPS-induced hPMVECs were abrogated. In conclusion, GLA alleviated LPS-induced inflammation, apoptosis and permeability injury in hPMVECs by inhibiting STAT3 signaling, which highlighted the potential therapeutic value of GLA in the treatment of pneumonia.
Keywords: STAT3; apoptosis; glaucocalyxin A; inflammation.
Copyright: © Cao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
