Vitamin D receptor deficiency increases systolic blood pressure by upregulating the renin-angiotensin system and autophagy
- PMID: 35369533
- PMCID: PMC8943549
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2022.11243
Vitamin D receptor deficiency increases systolic blood pressure by upregulating the renin-angiotensin system and autophagy
Abstract
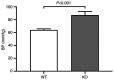
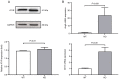
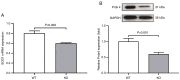
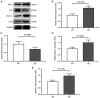
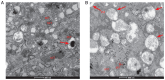
The vitamin D receptor (VDR) may regulate blood pressure via multiple pathways. The present study investigated the underlying mechanism by which VDR deficiency increases blood pressure. A total of 16 8-week-old male littermate mice were randomly divided into the VDR knockout and wild-type groups (VDR-/- and VDR+/+ , respectively). Blood pressure was measured using a four-channel PowerLab data acquisition and ADI software analysis system. After euthanasia, vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) were isolated from the VDR-/- and VDR+/+ mice. Oxidative stress, renin-angiotensin system (RAS) activation and autophagy markers were measured in the isolated VSMCs using reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR), western blotting and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) assays. Mean systolic pressure was significantly higher in the VDR-/- mice compared with the VDR+/+ mice. RT-qPCR and western blotting analyses indicated that RAS markers (angiotensin II and II type 1 receptor) were significantly upregulated, oxidative stress was increased (evidenced by reduced superoxide dismutase and peroxiredoxin-4) and autophagy was activated (upregulation of autophagy related protein 7, Beclin 1 and microtubule-associated proteins 1A/1B light chain 3A) in the VDR-/- VSMCs compared with the VDR+/+ VSMCs. TEM demonstrated that there were more autophagy bodies in the VDR-/- VSMCs compared with the VDR+/+ VSMCs. In conclusion, VDR deficiency was associated with high blood pressure. The mechanism underlying the increase in blood pressure caused by VDR deficiency may involve activation of the RAS, as well as increased oxidative stress and autophagy of VSMCs.
Keywords: autophagy; hypertension; oxidative stress; vascular smooth muscle cell; vitamin D receptor.
Copyright: © Jia et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Yuan W, Pan W, Kong J, Zheng W, Szeto FL, Wong KE, Cohen R, Klopot A, Zhang Z, Li YC. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 suppresses renin gene transcription by blocking the activity of the cyclic AMP response element in the renin gene promoter. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:29821–29830. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705495200. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
