A novel KLF13 mutation underlying congenital patent ductus arteriosus and ventricular septal defect, as well as bicuspid aortic valve
- PMID: 35369534
- PMCID: PMC8943534
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2022.11240
A novel KLF13 mutation underlying congenital patent ductus arteriosus and ventricular septal defect, as well as bicuspid aortic valve
Abstract
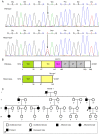
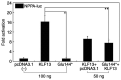
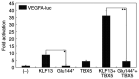
Recently, mutations in the Kruppel-like factor 13 (KLF13) gene encoding a Kruppel-like transcription factor have been reported to cause congenital heart disease (CHD). However, due to pronounced genetic heterogeneity, the mutational spectrum of KLF13 in other cohorts of cases suffering from distinct types of CHD remain to be ascertained. In the present investigation, by Sanger sequencing of KLF13 in 316 unrelated cases affected by different forms of CHD, a new mutation in heterozygous status, NM_015995.3: c.430G>T; p.(Glu144*), was detected in an index patient affected with patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) and ventricular septal defect (VSD), as well as bicuspid aortic valve (BAV), with a mutation frequency of ~0.32%. Genetic investigation of the available family members of the proband demonstrated that the truncating mutation co-segregated with CHD. The nonsense mutation was not observed in 400 unrelated volunteers without CHD who were enrolled as control subjects. Quantitative biological measurements with dual luciferase reporters revealed that Glu144*-mutant KLF13 did not transactivate the downstream genes vascular endothelial growth factor A and natriuretic peptide A. In addition, the mutation abrogated the synergistic transcriptional activation between KLF13 and T-box transcription factor 5, a well-established CHD-causing gene. In conclusion, the present study indicates that genetically defective KLF13 contributes to familial PDA and VSD, as well as BAV, which expands the phenotypic spectrum linked to KLF13, and reveals a novel molecular pathogenesis of the disease, providing a new molecular target for the early prophylaxis and individualized treatment of CHD.
Keywords: KLF13; biochemical assay; congenital heart defect; molecular genetics; transgene.
Copyright: © Abhinav et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
KLF13 loss-of-function variation contributes to familial congenital heart defects.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Nov;24(21):11273-11285. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202011_23617. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33215447
-
A New TBX5 Loss-of-Function Mutation Contributes to Congenital Heart Defect and Atrioventricular Block.Int Heart J. 2020 Jul 30;61(4):761-768. doi: 10.1536/ihj.19-650. Epub 2020 Jul 8. Int Heart J. 2020. PMID: 32641638
-
MEF2C loss-of-function mutation contributes to congenital heart defects.Int J Med Sci. 2017 Sep 8;14(11):1143-1153. doi: 10.7150/ijms.21353. eCollection 2017. Int J Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 29104469 Free PMC article.
-
The incidence of congenital heart disease.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002 Jun 19;39(12):1890-900. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(02)01886-7. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002. PMID: 12084585 Review.
-
Molecular determinants of atrial and ventricular septal defects and patent ductus arteriosus.Am J Med Genet. 2000 Winter;97(4):304-9. doi: 10.1002/1096-8628(200024)97:4<304::aid-ajmg1281>3.0.co;2-#. Am J Med Genet. 2000. PMID: 11376442 Review.
Cited by
-
Somatic GATA4 mutation contributes to tetralogy of Fallot.Exp Ther Med. 2024 Jan 8;27(2):91. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12379. eCollection 2024 Feb. Exp Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 38274337 Free PMC article.
-
The Involvement of Krüppel-like Factors in Cardiovascular Diseases.Life (Basel). 2023 Feb 2;13(2):420. doi: 10.3390/life13020420. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is the Cis-Element CACCC-Box a Master Regulatory Element during Cardiovascular Disease? A Bioinformatics Approach from the Perspective of the Krüppel-like Family of Transcription Factors.Life (Basel). 2024 Apr 11;14(4):493. doi: 10.3390/life14040493. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38672763 Free PMC article.
-
Krüppel-like Factor-9 and Krüppel-like Factor-13: Highly Related, Multi-Functional, Transcriptional Repressors and Activators of Oncogenesis.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 30;15(23):5667. doi: 10.3390/cancers15235667. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery and functional investigation of BMP4 as a new causative gene for human congenital heart disease.Am J Transl Res. 2024 May 15;16(5):2034-2048. doi: 10.62347/DGCD4269. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38883374 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, Chamberlain AM, Chang AR, Cheng S, Das SR, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2019 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139:e56–e528. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000659. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Skeffington KL, Bond AR, Bigotti MG, AbdulGhani S, Iacobazzi D, Kang SL, Heesom KJ, Wilson MC, Stoica S, Martin R, et al. Changes in inflammation and oxidative stress signalling pathways in coarcted aorta triggered by bicuspid aortic valve and growth in young children. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(48) doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9171. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
