Circular RNAs as Diagnostic and Prognostic Indicators of Colorectal Cancer: A Pooled Analysis of Individual Studies
- PMID: 35369570
- PMCID: PMC8967936
- DOI: 10.3389/pore.2022.1610037
Circular RNAs as Diagnostic and Prognostic Indicators of Colorectal Cancer: A Pooled Analysis of Individual Studies
Abstract
Background: Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have proven as a special subset of endogenous RNAs that are implicated in the tumorigenesis of various cancers. This study sought to evaluate the role of circRNAs in the diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer (CRC). Methods: The online databases were searched for collecting relevant studies on circRNAs as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers of CRC. Two researchers independently screened literature, extracted data, and evaluated the bias and risks of included studies. The diagnostic and prognostic indicators were merged and analyzed using STATA 12.0 software, and sources of heterogeneity were traced by the sensitivity analysis and the meta-regression test. Results: A total of 29 articles representing 2639 CRC patients were included. The pooled sensitivity, specificity, and area under the curve (AUC) of circRNAs in differentiating CRC from non-tumor control were 0.75 (95% CI: 0.69-0.80) and 0.74 (95% CI: 0.69-0.78) and 0.81, respectively. The survival analysis showed that up-regulations of up-regulated circRNAs were significantly related to dismal survival in CRC patients (HR = 2.38, p < 0.001). A stratified analysis showed that the comprehensive diagnostic value of up-regualted circRNAs in CRC was higher than that of down-regualted circRNAs (AUC: 0.83 vs. 0.77; Z test, p < 0.05). The efficacy of tissue-derived circRNAs in the diagnosis of CRC was equal to that of plasma/serum-derived ones (AUC: 0.81 vs. 0.82; Z test, p > 0.05). Conclusion: Abnormally expressed circRNAs as auxiliary biomarkers present underlying value in the diagnosis and prognosis prediction of CRC.
Keywords: circular RNA; colorectal cancer; diagnosis; pooled analysis; prognosis.
Copyright © 2022 Long, Xu, Ding, Huang and Ji.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
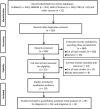
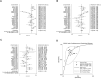



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

