Association Between Indoxyl Sulfate and Dialysis Initiation and Cardiac Outcomes in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients
- PMID: 35370416
- PMCID: PMC8967989
- DOI: 10.2147/IJNRD.S354658
Association Between Indoxyl Sulfate and Dialysis Initiation and Cardiac Outcomes in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients
Abstract
Introduction: Indoxyl sulfate, a protein-bound uremic toxin, has been reported as an atherosclerosis and fibrosis accelerator. This study aimed to determine whether serum indoxyl sulfate is associated with cardiac abnormalities, cardiovascular events, and renal progression to dialysis in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Methods: The prospective study enrolled 89 patients with CKD stage 3 to 5 patients. Serum biochemistry data and indoxyl sulfate were measured. All patients underwent echocardiographic examination. Global longitudinal strain (GLS) was calculated using two-dimensional speckle tracking. The clinical outcomes including cardiovascular event and dialysis initiation were recorded during a 2-year follow-up.
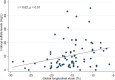
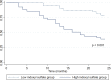
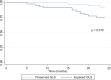
Results: Patients were divided into 2 groups based on the median value of serum indoxyl sulfate (low and high indoxyl sulfate groups). Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed that patients with higher indoxyl sulfate (≥6.124 mg/L) were significantly associated with renal progression to dialysis (p < 0.001). There was no significant difference in cardiovascular events between 2 groups (p = 0.082). In addition, serum indoxyl sulfate level was independently associated with GLS (r = 0.62; p = 0.01). The risk of cardiovascular events was significantly higher in patients with impaired GLS (>-16%) (p = 0.015).
Conclusion: Serum indoxyl sulfate level was a significant predictor for CKD progression to dialysis and was correlated with GLS, a speckle tracking echocardiography parameter representing early LV systolic dysfunction. Furthermore, GLS was associated with cardiovascular events in CKD patients. Serum indoxyl sulfate measurement may help to identify the high dialysis and cardiovascular risk CKD patients beyond traditional risk factors.
Keywords: cardiovascular events; chronic kidney disease; echocardiographic parameters; indoxyl sulfate; renal outcomes.
© 2022 Takkavatakarn et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Indoxyl sulfate predicts cardiovascular disease and renal function deterioration in advanced chronic kidney disease.Arch Med Res. 2012 Aug;43(6):451-6. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2012.08.002. Epub 2012 Aug 8. Arch Med Res. 2012. PMID: 22885091
-
Protein-bound uremic toxin lowering strategies in chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Nephrol. 2021 Dec;34(6):1805-1817. doi: 10.1007/s40620-020-00955-2. Epub 2021 Jan 23. J Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33484425
-
Indoxyl sulfate - the uremic toxin linking hemostatic system disturbances with the prevalence of cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic kidney disease.BMC Nephrol. 2017 Jan 25;18(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12882-017-0457-1. BMC Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28122514 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Indoxyl Sulfate on Progenitor Cell-Related Neovascularization of Peripheral Arterial Disease and Post-Angioplasty Thrombosis of Dialysis Vascular Access.Toxins (Basel). 2017 Jan 7;9(1):25. doi: 10.3390/toxins9010025. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28067862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Serum Indoxyl Sulfate on One-Year Adverse Events in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients with Heart Failure.J Clin Med. 2024 Jul 26;13(15):4384. doi: 10.3390/jcm13154384. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39124652 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Predictive value of protein-bound uremic toxins for heart failure in patients with chronic kidney disease.ESC Heart Fail. 2024 Feb;11(1):466-474. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14566. Epub 2023 Dec 2. ESC Heart Fail. 2024. PMID: 38041505 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of Indoxyl Sulfate Accumulation Reduces Renal Fibrosis in Sulfotransferase 1a1-Deficient Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 11;24(14):11329. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411329. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511089 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of indoxyl sulfate in biological fluids with emphasis on sample preparation techniques: A comprehensive analytical review.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 23;10(15):e35032. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35032. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39157307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-omics analysis of bariatric surgery's impact on type 2 diabetes and prediabetes.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 9;15(1):29215. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14577-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40783429 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiota-friendly diet ameliorates hypoalbuminemia in chronic kidney disease: evidence from NHANES.Front Immunol. 2025 May 6;16:1546031. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1546031. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40396178 Free PMC article.
References
-
- System USRD. 2020 USRDS Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

